gLOP: the global and Local Penalty for Capturing Predictive Heterogeneity
Paper and Code
Jul 29, 2016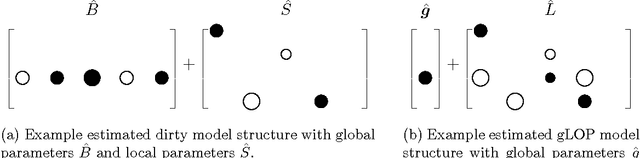
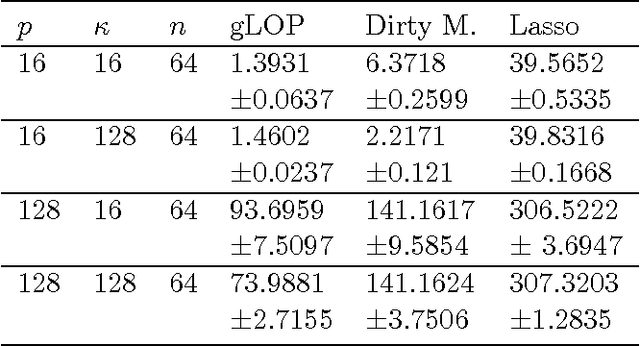
When faced with a supervised learning problem, we hope to have rich enough data to build a model that predicts future instances well. However, in practice, problems can exhibit predictive heterogeneity: most instances might be relatively easy to predict, while others might be predictive outliers for which a model trained on the entire dataset does not perform well. Identifying these can help focus future data collection. We present gLOP, the global and Local Penalty, a framework for capturing predictive heterogeneity and identifying predictive outliers. gLOP is based on penalized regression for multitask learning, which improves learning by leveraging training signal information from related tasks. We give two optimization algorithms for gLOP, one space-efficient, and another giving the full regularization path. We also characterize uniqueness in terms of the data and tuning parameters, and present empirical results on synthetic data and on two health research problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge