Generalized Linear Tree Space Nearest Neighbor
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2021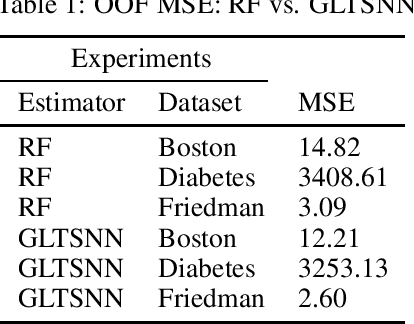
We present a novel method of stacking decision trees by projection into an ordered time split out-of-fold (OOF) one nearest neighbor (1NN) space. The predictions of these one nearest neighbors are combined through a linear model. This process is repeated many times and averaged to reduce variance. Generalized Linear Tree Space Nearest Neighbor (GLTSNN) is competitive with respect to Mean Squared Error (MSE) compared to Random Forest (RF) on several publicly available datasets. Some of the theoretical and applied advantages of GLTSNN are discussed. We conjecture a classifier based upon the GLTSNN would have an error that is asymptotically bounded by twice the Bayes error rate like k = 1 Nearest Neighbor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge