From "um" to "yeah": Producing, predicting, and regulating information flow in human conversation
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2024
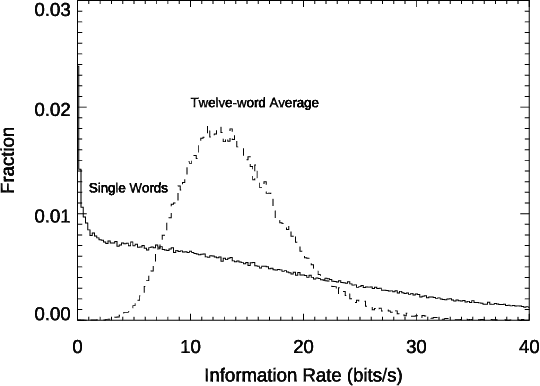
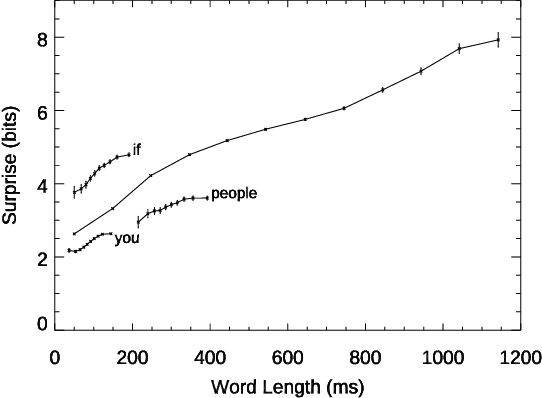
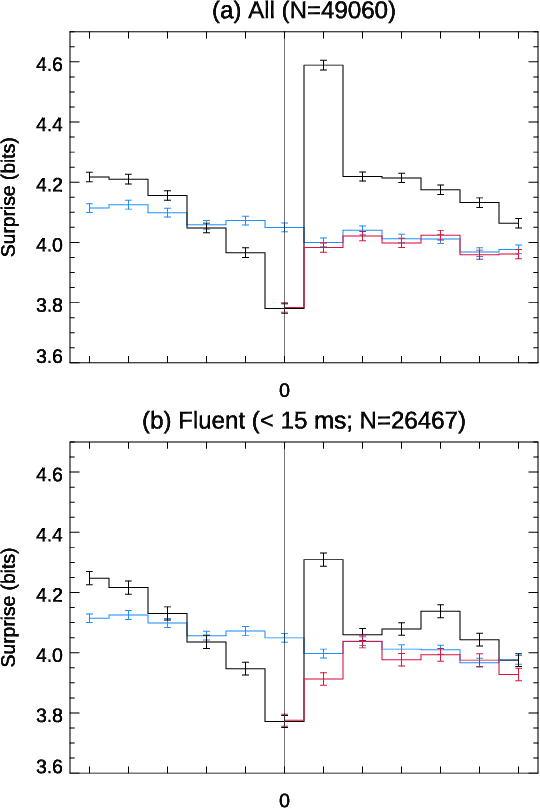
Conversation demands attention. Speakers must call words to mind, listeners must make sense of them, and both together must negotiate this flow of information, all in fractions of a second. We used large language models to study how this works in a large-scale dataset of English-language conversation, the CANDOR corpus. We provide a new estimate of the information density of unstructured conversation, of approximately 13 bits/second, and find significant effects associated with the cognitive load of both retrieving, and presenting, that information. We also reveal a role for backchannels -- the brief yeahs, uh-huhs, and mhmms that listeners provide -- in regulating the production of novelty: the lead-up to a backchannel is associated with declining information rate, while speech downstream rebounds to previous rates. Our results provide new insights into long-standing theories of how we respond to fluctuating demands on cognitive resources, and how we negotiate those demands in partnership with others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge