From Simulation to Real World Maneuver Execution using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
May 13, 2020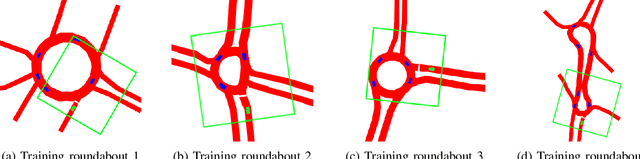
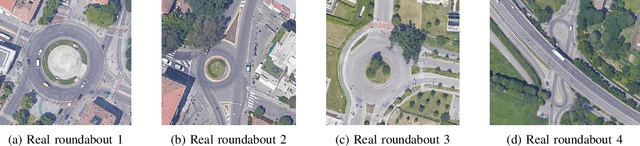
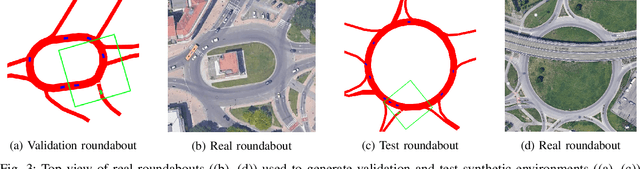
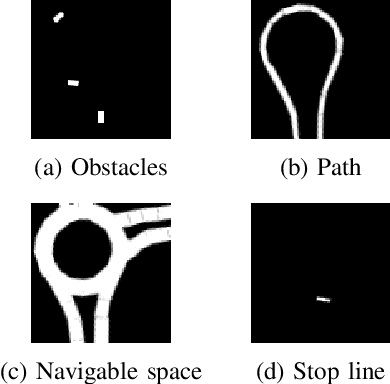
Deep Reinforcement Learning has proved to be able to solve many control tasks in different fields, but the behavior of these systems is not always as expected when deployed in real-world scenarios. This is mainly due to the lack of domain adaptation between simulated and real-world data together with the absence of distinction between train and test datasets. In this work, we investigate these problems in the autonomous driving field, especially for a maneuver planning module for roundabout insertions. In particular, we present a system based on multiple environments in which agents are trained simultaneously, evaluating the behavior of the model in different scenarios. Finally, we analyze techniques aimed at reducing the gap between simulated and real-world data showing that this increased the generalization capabilities of the system both on unseen and real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge