FlowSAN: Privacy-enhancing Semi-Adversarial Networks to Confound Arbitrary Face-based Gender Classifiers
Paper and Code
May 03, 2019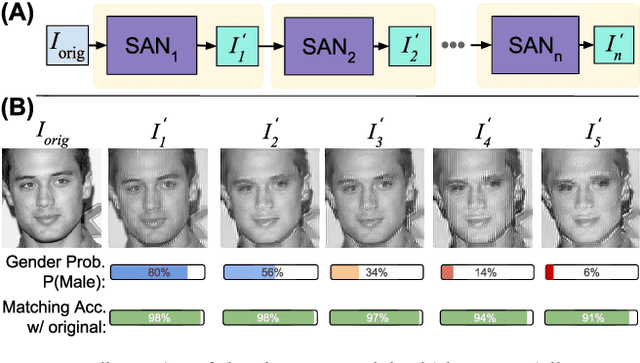

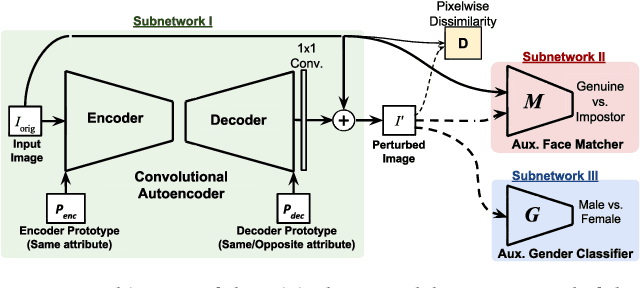
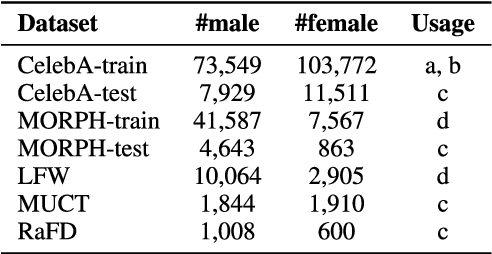
Privacy concerns in the modern digital age have prompted researchers to develop techniques that allow users to selectively suppress certain information in collected data while allowing for other information to be extracted. In this regard, Semi-Adversarial Networks (SAN) have recently emerged as a method for imparting soft-biometric privacy to face images. SAN enables modifications of input face images so that the resulting face images can still be reliably used by arbitrary conventional face matchers for recognition purposes, while attribute classifiers, such as gender classifiers, are confounded. However, the generalizability of SANs across arbitrary gender classifiers has remained an open concern. In this work, we propose a new method, FlowSAN, for allowing SANs to generalize to multiple unseen gender classifiers. We propose combining a diverse set of SAN models to compensate each other's weaknesses, thereby, forming a robust model with improved generalization capability. Extensive experiments using different unseen gender classifiers and face matchers demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed paradigm in imparting gender privacy to face images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge