Flexible Behavior Trees: In search of the mythical HFSMBTH for Collaborative Autonomy in Robotics
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2022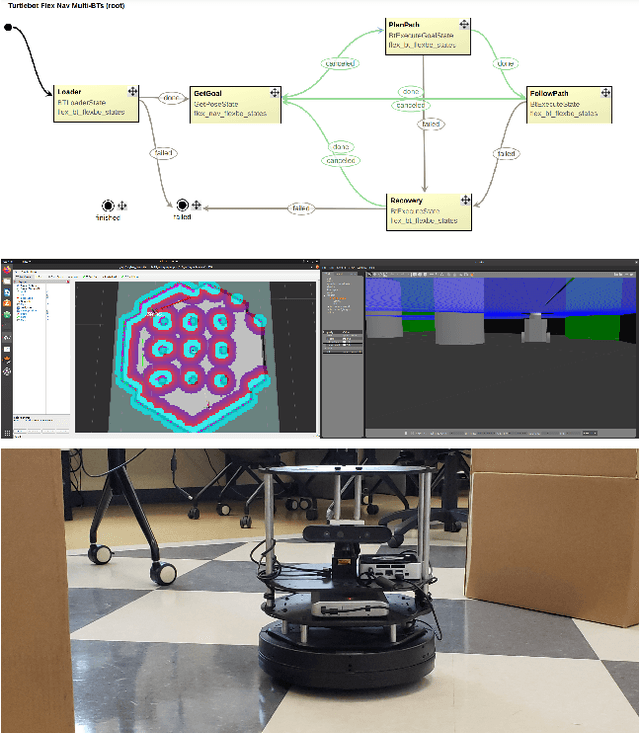
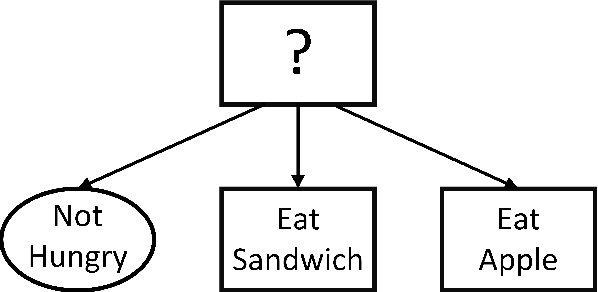
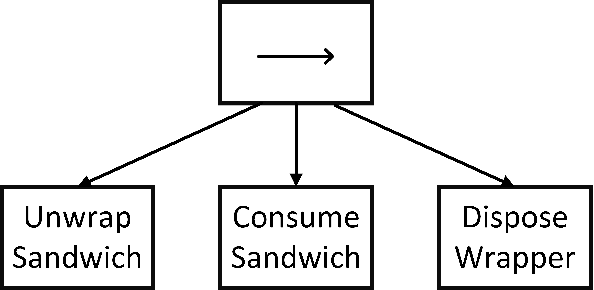
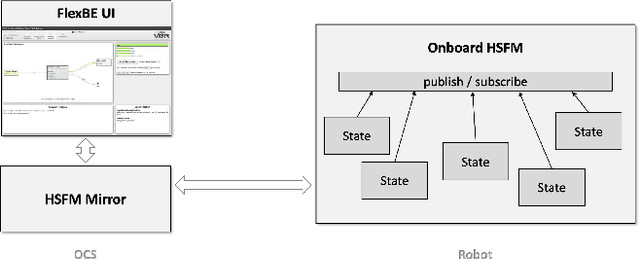
In recent years, the model of computation known as Behavior Trees (BT), first developed in the video game industry, has become more popular in the robotics community for defining discrete behavior switching. BTs are threatening to supplant the venerable Hierarchical Finite State Machine (HFSM) model. In this paper we contrast BT and HFSM, pointing out some potential issues with the BT form, and advocate for a hybrid model of computation that uses both BT and HFSM in ways that leverage their individual strengths. The work introduces a new open-source package for ROS 2 that extends the Flexible Behavior Engine (FlexBE) to enable interaction with BT-based behaviors within a HFSM in a way that supports collaborative autonomy. Simulation and hardware demonstrations illustrate the concepts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge