Few-shot Learning in Emotion Recognition of Spontaneous Speech Using a Siamese Neural Network with Adaptive Sample Pair Formation
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2021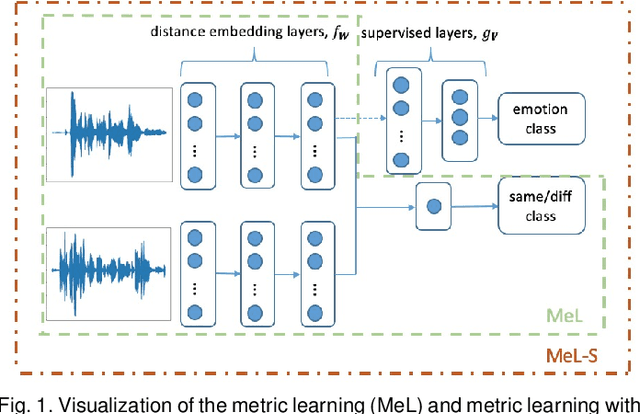

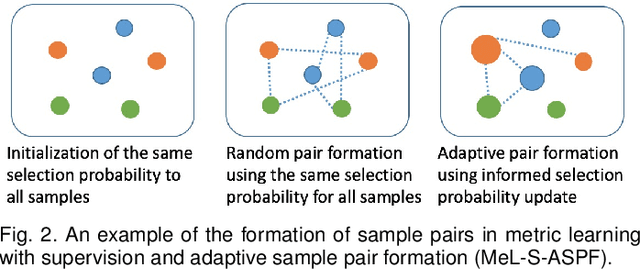
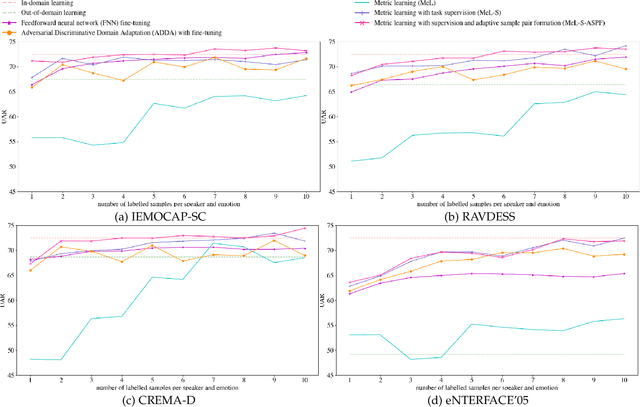
Speech-based machine learning (ML) has been heralded as a promising solution for tracking prosodic and spectrotemporal patterns in real-life that are indicative of emotional changes, providing a valuable window into one's cognitive and mental state. Yet, the scarcity of labelled data in ambulatory studies prevents the reliable training of ML models, which usually rely on "data-hungry" distribution-based learning. Leveraging the abundance of labelled speech data from acted emotions, this paper proposes a few-shot learning approach for automatically recognizing emotion in spontaneous speech from a small number of labelled samples. Few-shot learning is implemented via a metric learning approach through a siamese neural network, which models the relative distance between samples rather than relying on learning absolute patterns of the corresponding distributions of each emotion. Results indicate the feasibility of the proposed metric learning in recognizing emotions from spontaneous speech in four datasets, even with a small amount of labelled samples. They further demonstrate superior performance of the proposed metric learning compared to commonly used adaptation methods, including network fine-tuning and adversarial learning. Findings from this work provide a foundation for the ambulatory tracking of human emotion in spontaneous speech contributing to the real-life assessment of mental health degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge