Feedback Delay Network Optimization
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2024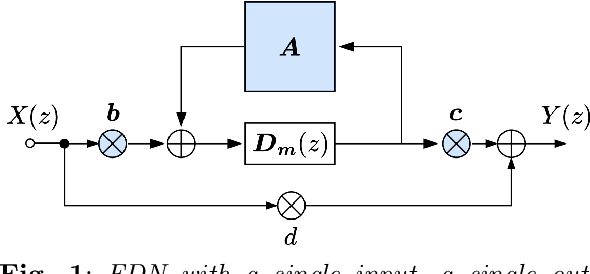

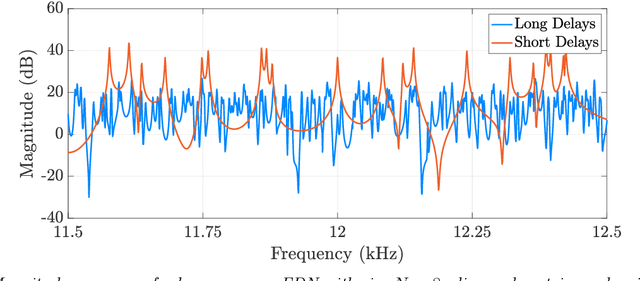

A common bane of artificial reverberation algorithms is spectral coloration, typically manifesting as metallic ringing, leading to a degradation in the perceived sound quality. This paper presents an optimization framework where a differentiable feedback delay network is used to learn a set of parameters to reduce coloration iteratively. The parameters under optimization include the feedback matrix, as well as the input and output gains. The optimization objective is twofold: to maximize spectral flatness through a spectral loss while maintaining temporal density by penalizing sparseness in the parameter values. A favorable narrower distribution of modal excitation is achieved while maintaining the desired impulse response density. In a subjective assessment, the new method proves effective in reducing perceptual coloration of late reverberation. The proposed method achieves computational savings compared to the baseline while preserving its performance. The effectiveness of this work is demonstrated through two application scenarios where natural-sounding synthetic impulse responses are obtained via the introduction of attenuation filters and an optimizable scattering feedback matrix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge