Feature Perturbation Augmentation for Reliable Evaluation of Importance Estimators
Paper and Code
Mar 02, 2023
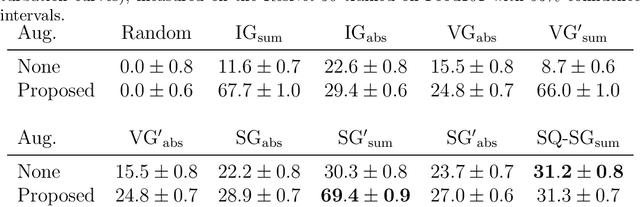
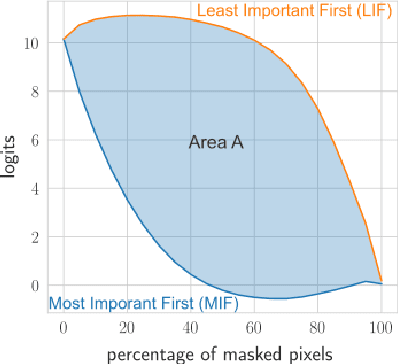
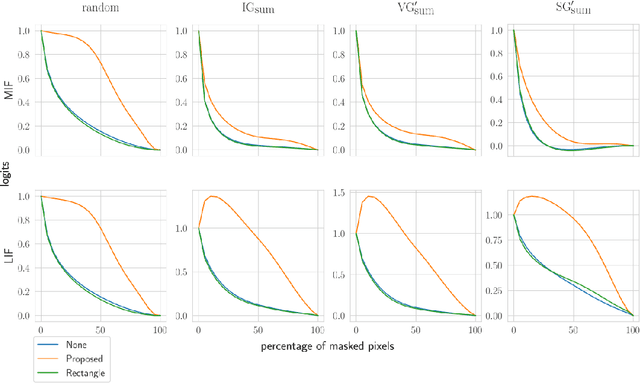
Post-hoc explanation methods attempt to make the inner workings of deep neural networks more interpretable. However, since a ground truth is in general lacking, local post-hoc interpretability methods, which assign importance scores to input features, are challenging to evaluate. One of the most popular evaluation frameworks is to perturb features deemed important by an interpretability method and to measure the change in prediction accuracy. Intuitively, a large decrease in prediction accuracy would indicate that the explanation has correctly quantified the importance of features with respect to the prediction outcome (e.g., logits). However, the change in the prediction outcome may stem from perturbation artifacts, since perturbed samples in the test dataset are out of distribution (OOD) compared to the training dataset and can therefore potentially disturb the model in an unexpected manner. To overcome this challenge, we propose feature perturbation augmentation (FPA) which creates and adds perturbed images during the model training. Through extensive computational experiments, we demonstrate that FPA makes deep neural networks (DNNs) more robust against perturbations. Furthermore, training DNNs with FPA demonstrate that the sign of importance scores may explain the model more meaningfully than has previously been assumed. Overall, FPA is an intuitive data augmentation technique that improves the evaluation of post-hoc interpretability methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge