Fast Glioblastoma Detection in Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images by Topological Explainable Automatic Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 23, 2020
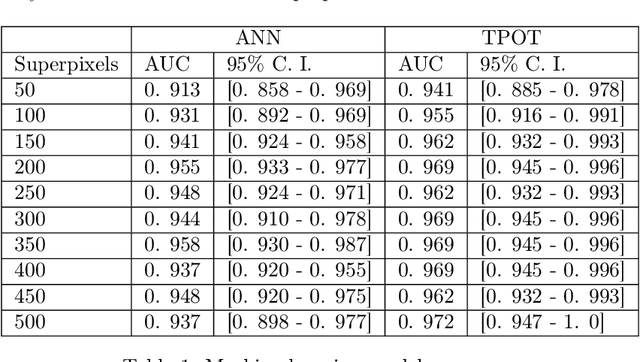
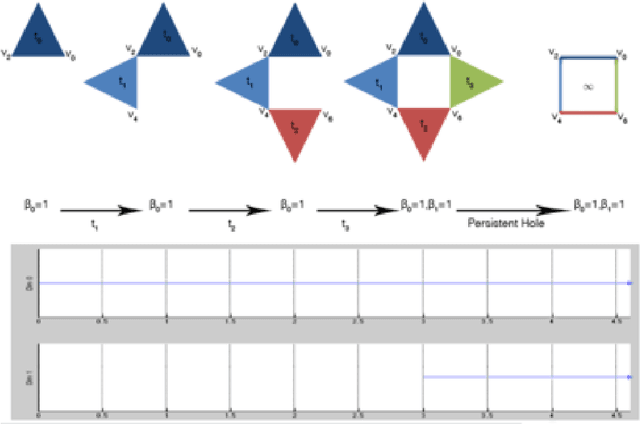
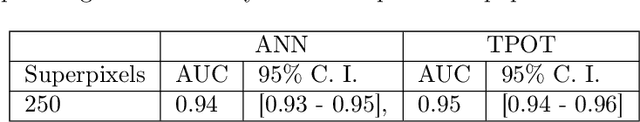
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a fast-growing and highly invasive brain tumor, it tends to occur in adults between the ages of 45 and 70 and it accounts for 52 percent of all primary brain tumors. Usually, GBMs are detected by magnetic resonance images (MRI). Among MRI images, Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence produces high quality digital tumor representation. Fast detection and segmentation techniques are needed for overcoming subjective medical doctors (MDs) judgment. In this work, a new framework for radiomics analysis of GBM on FLAIR images is proposed. The framework can be used both for an initial detection of GBM and in case for its segmentation. The novelty of the methodology is the combination of new topological features computed by topological data analysis, textural features and of automatic interpretable machine learning algorithm. The framework was evaluated on a public available dataset and it reaches up to the 97% of accuracy on the detection task and up to 95% of accuracy on the segmentation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge