Fairness based Multi-Preference Resource Allocation in Decentralised Open Markets
Paper and Code
Sep 01, 2021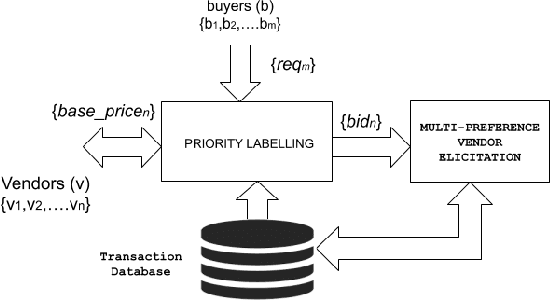
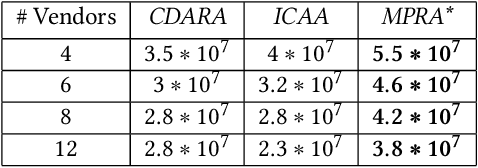
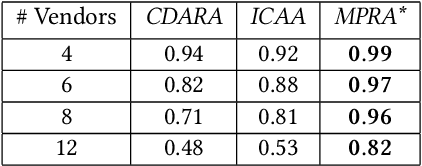
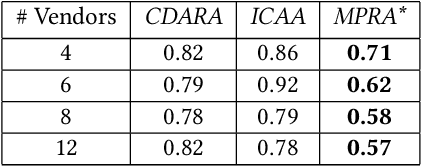
In this work, we focus on resource allocation in a decentralised open market. In decentralised open markets consists of multiple vendors and multiple dynamically-arriving buyers, thus makes the market complex and dynamic. Because, in these markets, negotiations among vendors and buyers take place over multiple conflicting issues such as price, scalability, robustness, delay, etc. As a result, optimising the resource allocation in such open markets becomes directly dependent on two key decisions, which are; incorporating a different kind of buyers' preferences, and fairness based vendor elicitation strategy. Towards this end, in this work, we propose a three-step resource allocation approach that employs a reverse-auction paradigm. At the first step, priority label is attached to each bidding vendor based on the proposed priority mechanism. Then, at the second step, the preference score is calculated for all the different kinds of preferences of the buyers. Finally, at the third step, based on the priority label of the vendor and the preference score winner is determined. Finally, we compare the proposed approach with two state-of-the-art resource pricing and allocation strategies. The experimental results show that the proposed approach outperforms the other two resource allocation approaches in terms of the independent utilities of buyers and the overall utility of the open market.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge