Face Attributes as Cues for Deep Face Recognition Understanding
Paper and Code
May 14, 2021

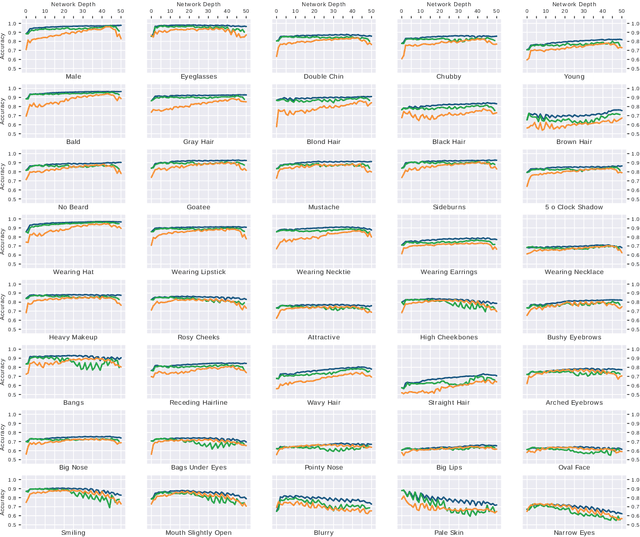

Deeply learned representations are the state-of-the-art descriptors for face recognition methods. These representations encode latent features that are difficult to explain, compromising the confidence and interpretability of their predictions. Most attempts to explain deep features are visualization techniques that are often open to interpretation. Instead of relying only on visualizations, we use the outputs of hidden layers to predict face attributes. The obtained performance is an indicator of how well the attribute is implicitly learned in that layer of the network. Using a variable selection technique, we also analyze how these semantic concepts are distributed inside each layer, establishing the precise location of relevant neurons for each attribute. According to our experiments, gender, eyeglasses and hat usage can be predicted with over 96% accuracy even when only a single neural output is used to predict each attribute. These performances are less than 3 percentage points lower than the ones achieved by deep supervised face attribute networks. In summary, our experiments show that, inside DCNNs optimized for face identification, there exists latent neurons encoding face attributes almost as accurately as DCNNs optimized for these attributes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge