Extraction of Product Specifications from the Web -- Going Beyond Tables and Lists
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2022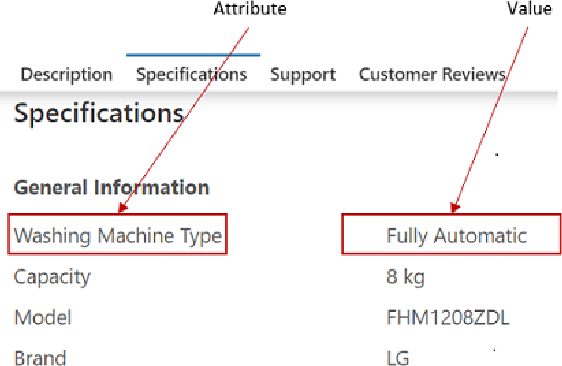
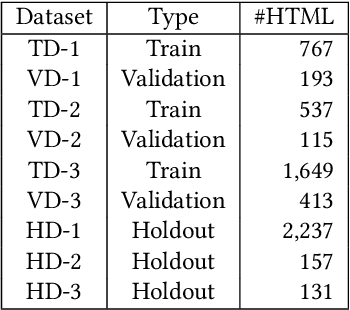

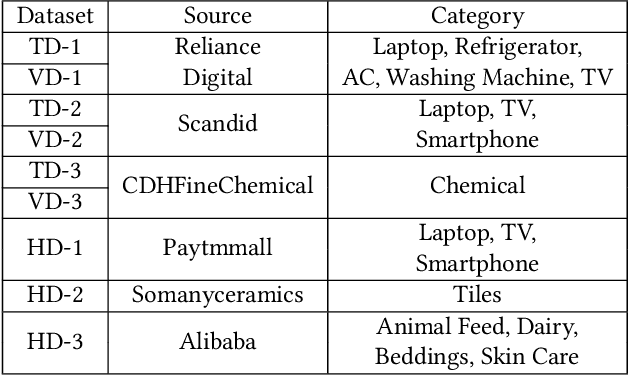
E-commerce product pages on the web often present product specification data in structured tabular blocks. Extraction of these product attribute-value specifications has benefited applications like product catalogue curation, search, question answering, and others. However, across different Websites, there is a wide variety of HTML elements (like <table>, <ul>, <div>, <span>, <dl> etc.) typically used to render these blocks that makes their automatic extraction a challenge. Most of the current research has focused on extracting product specifications from tables and lists and, therefore, suffers from recall when applied to a large-scale extraction setting. In this paper, we present a product specification extraction approach that goes beyond tables or lists and generalizes across the diverse HTML elements used for rendering specification blocks. Using a combination of hand-coded features and deep learned spatial and token features, we first identify the specification blocks on a product page. We then extract the product attribute-value pairs from these blocks following an approach inspired by wrapper induction. We created a labeled dataset of product specifications extracted from 14,111 diverse specification blocks taken from a range of different product websites. Our experiments show the efficacy of our approach compared to the current specification extraction models and support our claim about its application to large-scale product specification extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge