Extracting and Validating Explanatory Word Archipelagoes using Dual Entropy
Paper and Code
Feb 22, 2020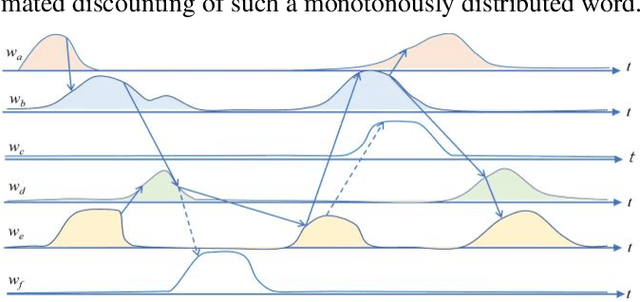
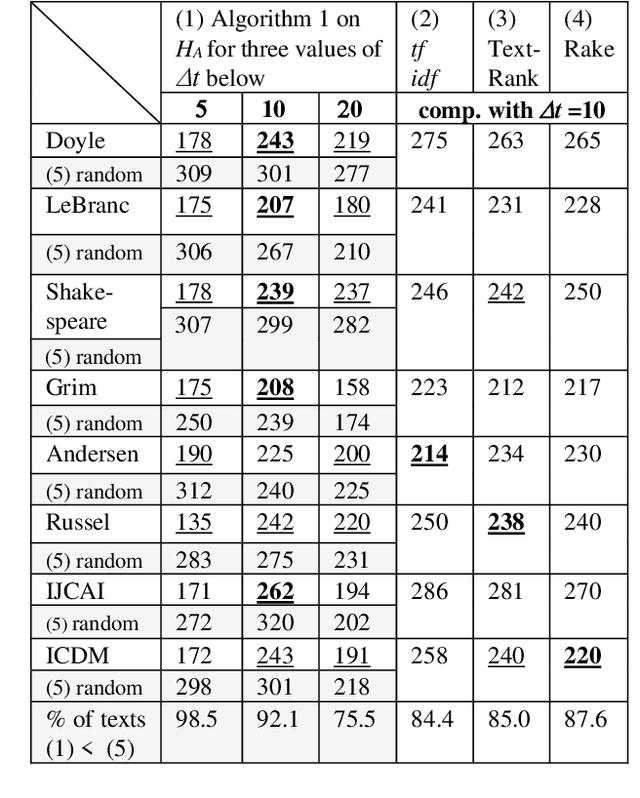
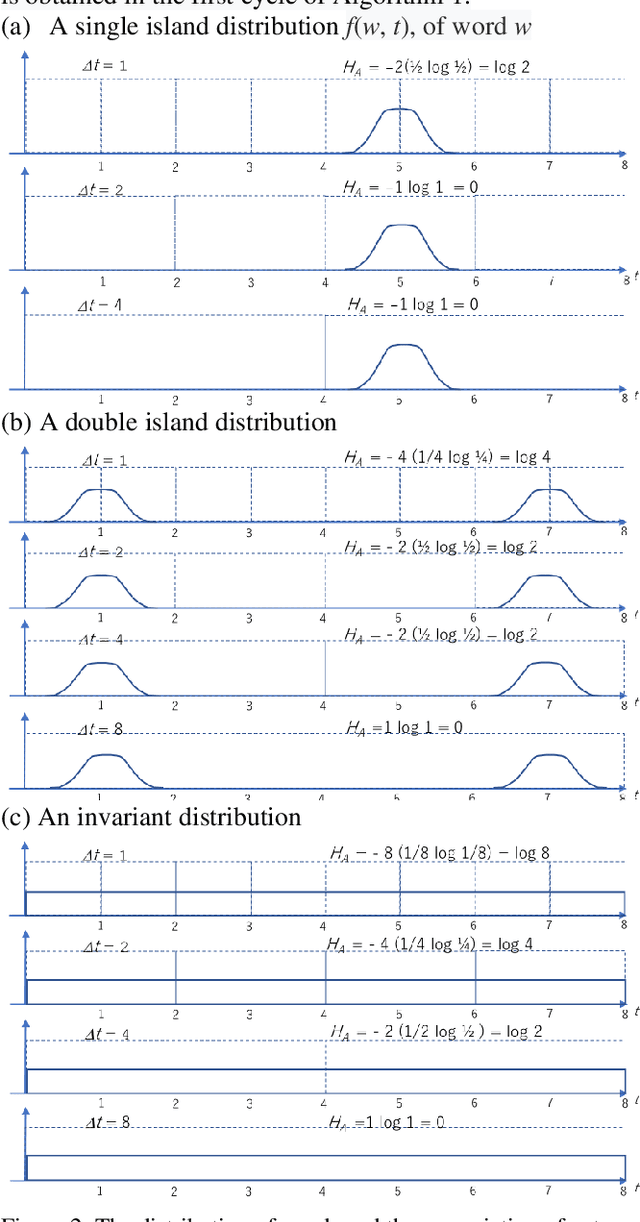
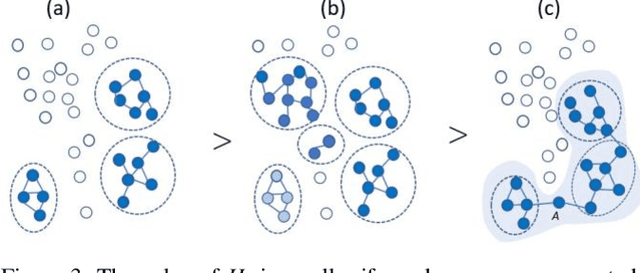
The logical connectivity of text is represented by the connectivity of words that form archipelagoes. Here, each archipelago is a sequence of islands of the occurrences of a certain word. An island here means the local sequence of sentences where the word is emphasized, and an archipelago of a length comparable to the target text is extracted using the co-variation of entropy A (the window-based entropy) on the distribution of the word's occurrences with the width of each time window. Then, the logical connectivity of text is evaluated on entropy B (the graph-based entropy) computed on the distribution of sentences to connected word-clusters obtained on the co-occurrence of words. The results show the parts of the target text with words forming archipelagoes extracted on entropy A, without learned or prepared knowledge, form an explanatory part of the text that is of smaller entropy B than the parts extracted by the baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge