Exploring Weaknesses of VQA Models through Attribution Driven Insights
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2020
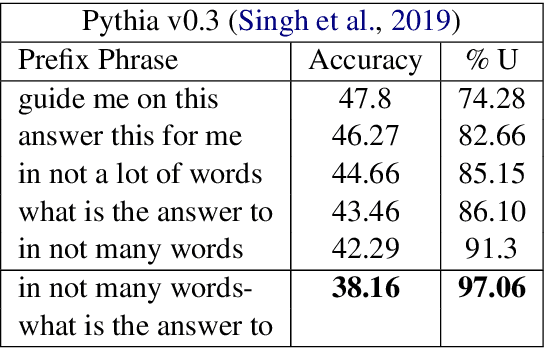

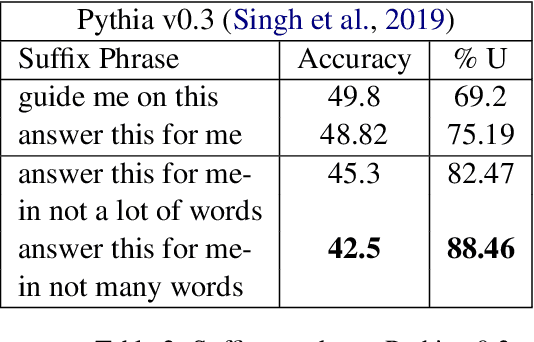
Deep Neural Networks have been successfully used for the task of Visual Question Answering for the past few years owing to the availability of relevant large scale datasets. However these datasets are created in artificial settings and rarely reflect the real world scenario. Recent research effectively applies these VQA models for answering visual questions for the blind. Despite achieving high accuracy these models appear to be susceptible to variation in input questions.We analyze popular VQA models through the lens of attribution (input's influence on predictions) to gain valuable insights. Further, We use these insights to craft adversarial attacks which inflict significant damage to these systems with negligible change in meaning of the input questions. We believe this will enhance development of systems more robust to the possible variations in inputs when deployed to assist the visually impaired.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge