Exploring Author Context for Detecting Intended vs Perceived Sarcasm
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2019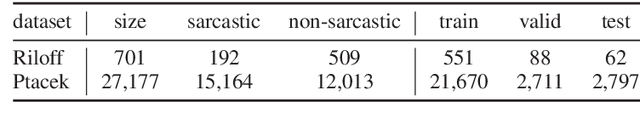
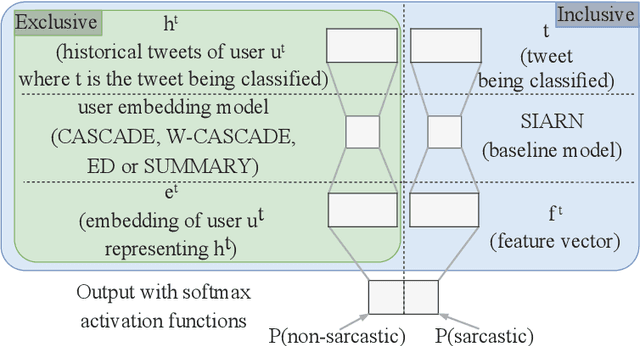
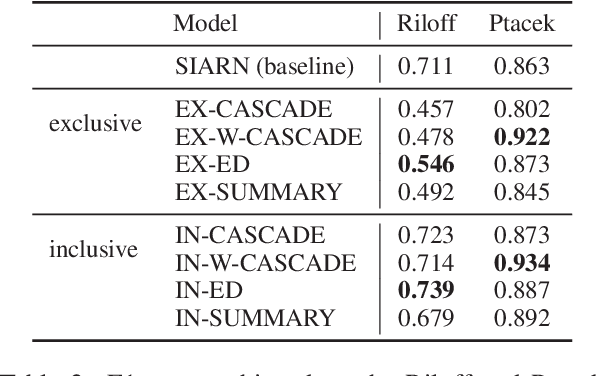
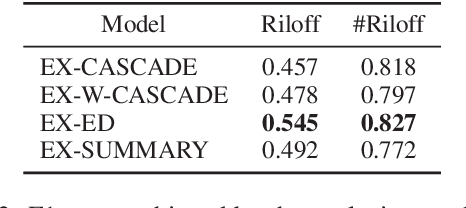
We investigate the impact of using author context on textual sarcasm detection. We define author context as the embedded representation of their historical posts on Twitter and suggest neural models that extract these representations. We experiment with two tweet datasets, one labelled manually for sarcasm, and the other via tag-based distant supervision. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on the second dataset, but not on the one labelled manually, indicating a difference between intended sarcasm, captured by distant supervision, and perceived sarcasm, captured by manual labelling.
* Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics, 2019, pages 2854-2859 * 6 pages, 1 figure, ACL 2020
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge