Explicit Basis Function Kernel Methods for Cloud Segmentation in Infrared Sky Images
Paper and Code
Feb 19, 2021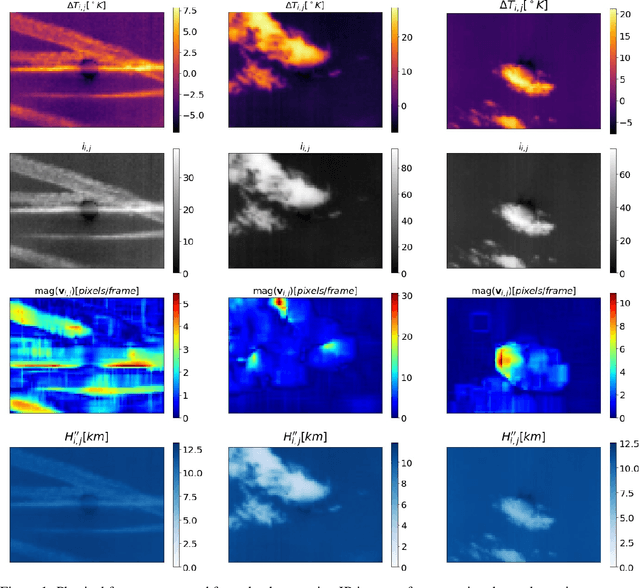
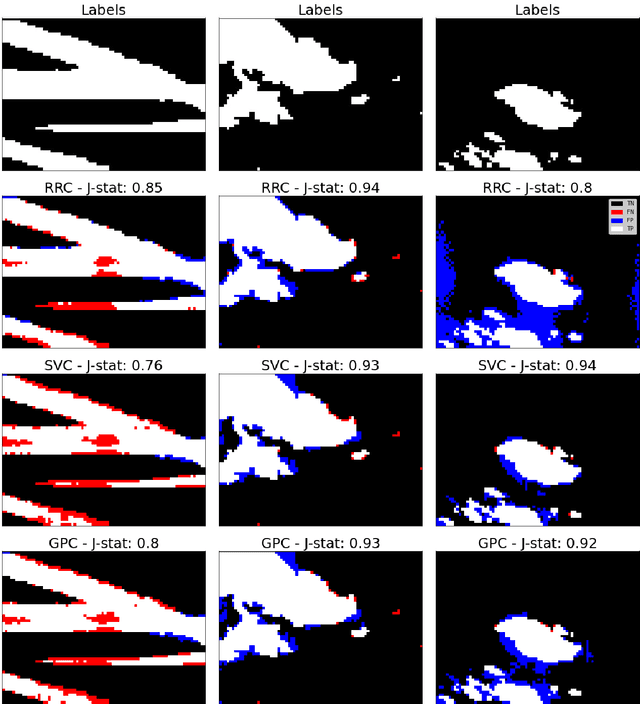
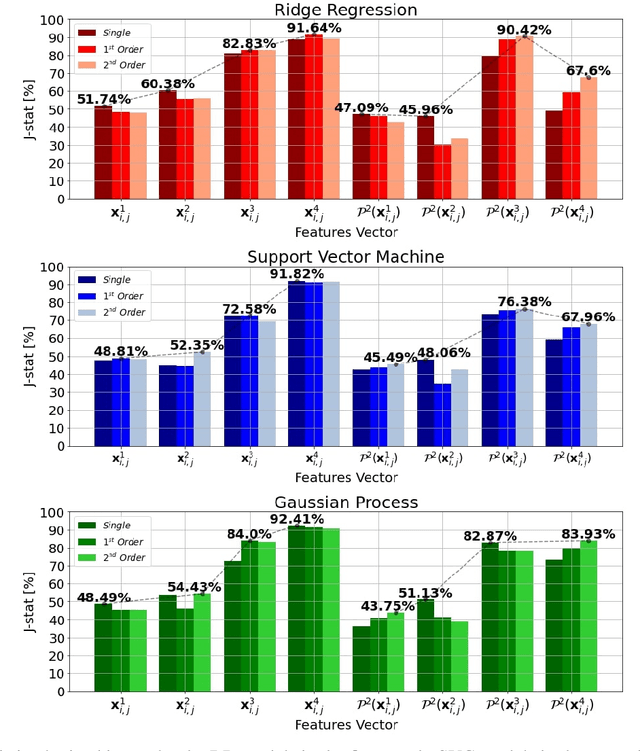

Photovoltaic (PV) systems are sensitive to cloud shadow projection, which needs to be forecasted to reduce the noise impacting the short-term forecast of Global Solar Irradiance (GSI). We present a comparison between different kernel discriminative models for cloud detection. The models are solved in the primal formulation to make them feasible in real-time applications. The performances are compared using the j-statistic. The Infrared (IR) images have been preprocessed to remove debris, which increases the performance of the analyzed methods. The use of the pixels neighboring features also leads to a performance improvement. Discriminative models solved in the primal yield a dramatically lower computing time along with high performance in the segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge