Explaining Results of Multi-Criteria Decision Making
Paper and Code
Sep 10, 2022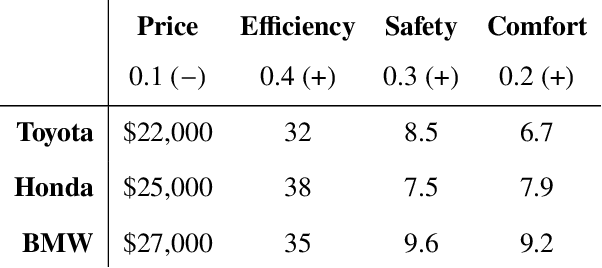

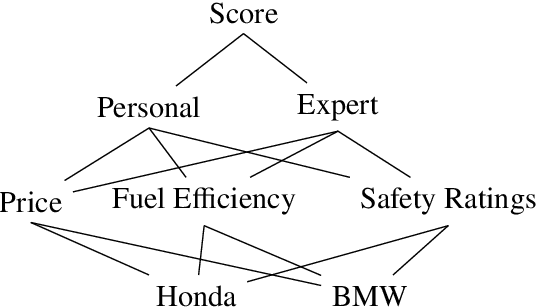

We introduce a method for explaining the results of various linear and hierarchical multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) techniques such as WSM and AHP. The two key ideas are (A) to maintain a fine-grained representation of the values manipulated by these techniques and (B) to derive explanations from these representations through merging, filtering, and aggregating operations. An explanation in our model presents a high-level comparison of two alternatives in an MCDM problem, presumably an optimal and a non-optimal one, illuminating why one alternative was preferred over the other one. We show the usefulness of our techniques by generating explanations for two well-known examples from the MCDM literature. Finally, we show their efficacy by performing computational experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge