Explainable Neural Network-based Modulation Classification via Concept Bottleneck Models
Paper and Code
Jan 04, 2021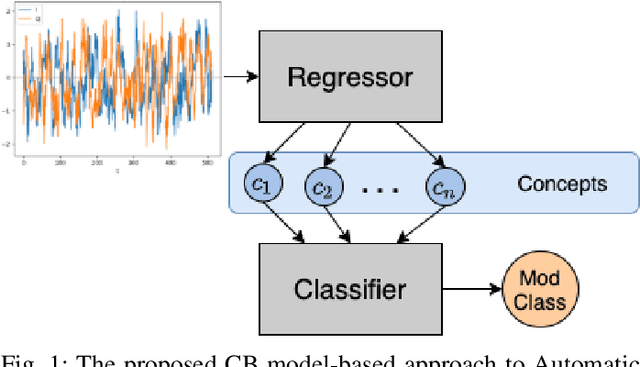
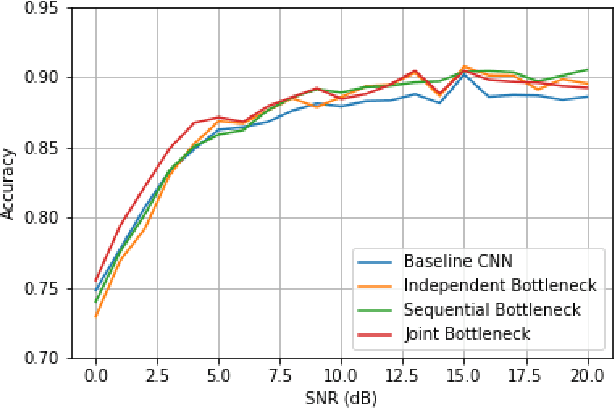
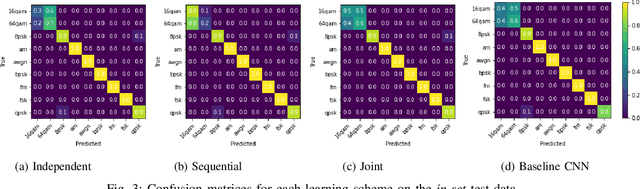
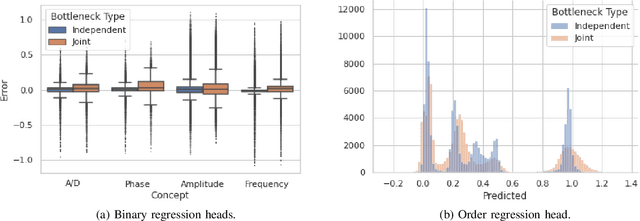
While RFML is expected to be a key enabler of future wireless standards, a significant challenge to the widespread adoption of RFML techniques is the lack of explainability in deep learning models. This work investigates the use of CB models as a means to provide inherent decision explanations in the context of DL-based AMC. Results show that the proposed approach not only meets the performance of single-network DL-based AMC algorithms, but provides the desired model explainability and shows potential for classifying modulation schemes not seen during training (i.e. zero-shot learning).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge