Explainable Disease Classification via weakly-supervised segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2020

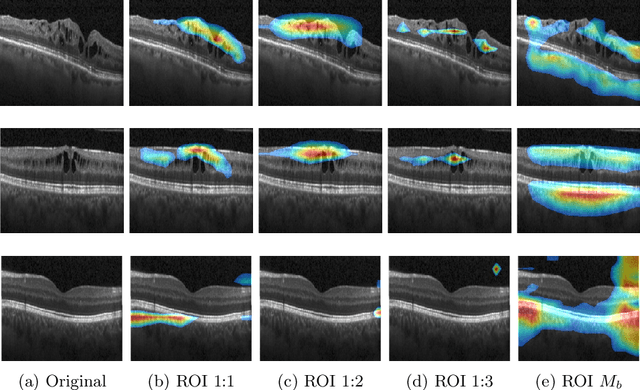

Deep learning based approaches to Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) typically pose the problem as an image classification (Normal or Abnormal) problem. These systems achieve high to very high accuracy in specific disease detection for which they are trained but lack in terms of an explanation for the provided decision/classification result. The activation maps which correspond to decisions do not correlate well with regions of interest for specific diseases. This paper examines this problem and proposes an approach which mimics the clinical practice of looking for an evidence prior to diagnosis. A CAD model is learnt using a mixed set of information: class labels for the entire training set of images plus a rough localisation of suspect regions as an extra input for a smaller subset of training images for guiding the learning. The proposed approach is illustrated with detection of diabetic macular edema (DME) from OCT slices. Results of testing on on a large public dataset show that with just a third of images with roughly segmented fluid filled regions, the classification accuracy is on par with state of the art methods while providing a good explanation in the form of anatomically accurate heatmap /region of interest. The proposed solution is then adapted to Breast Cancer detection from mammographic images. Good evaluation results on public datasets underscores the generalisability of the proposed solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge