Experience Selection Using Dynamics Similarity for Efficient Multi-Source Transfer Learning Between Robots
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2020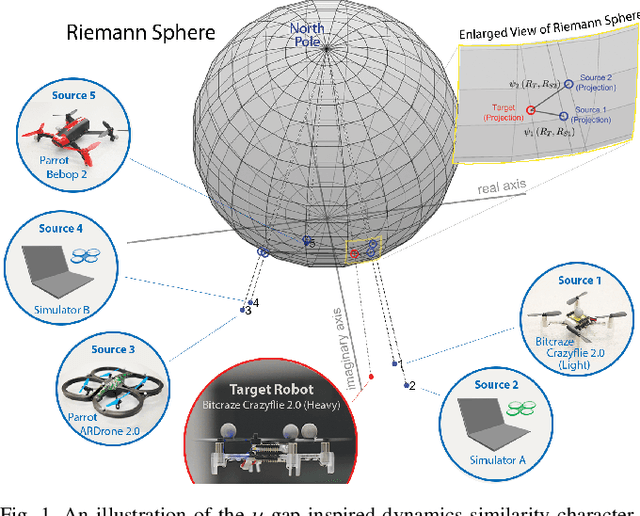
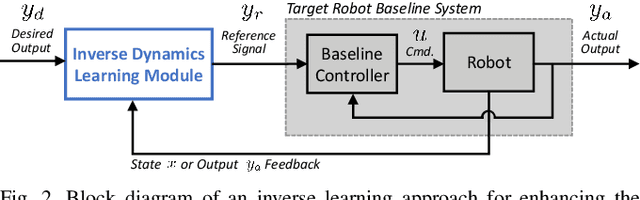
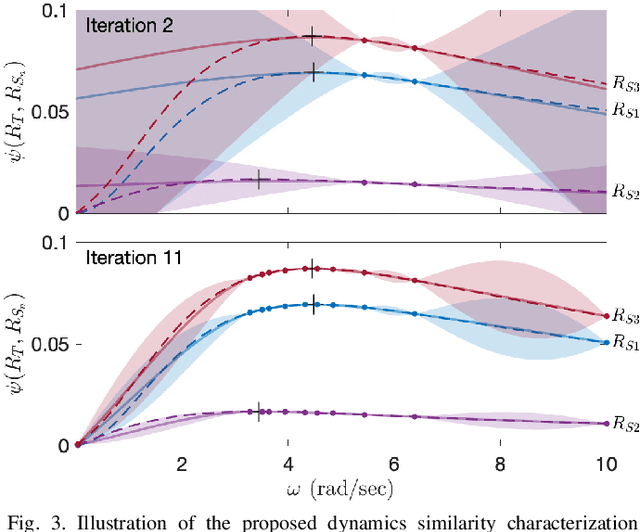
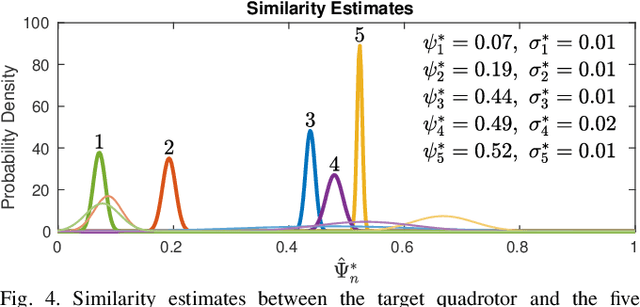
In the robotics literature, different knowledge transfer approaches have been proposed to leverage the experience from a source task or robot -- real or virtual -- to accelerate the learning process on a new task or robot. A commonly made but infrequently examined assumption is that incorporating experience from a source task or robot will be beneficial. In practice, inappropriate knowledge transfer can result in negative transfer or unsafe behaviour. In this work, inspired by a system gap metric from robust control theory, the $\nu$-gap, we present a data-efficient algorithm for estimating the similarity between pairs of robot systems. In a multi-source inter-robot transfer learning setup, we show that this similarity metric allows us to predict relative transfer performance and thus informatively select experiences from a source robot before knowledge transfer. We demonstrate our approach with quadrotor experiments, where we transfer an inverse dynamics model from a real or virtual source quadrotor to enhance the tracking performance of a target quadrotor on arbitrary hand-drawn trajectories. We show that selecting experiences based on the proposed similarity metric effectively facilitates the learning of the target quadrotor, improving performance by 62% compared to a poorly selected experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge