Example and Feature importance-based Explanations for Black-box Machine Learning Models
Paper and Code
Dec 21, 2018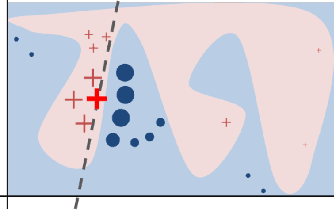
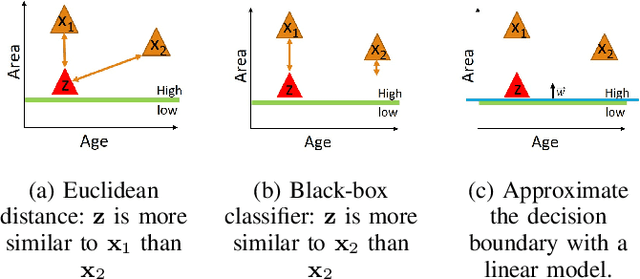
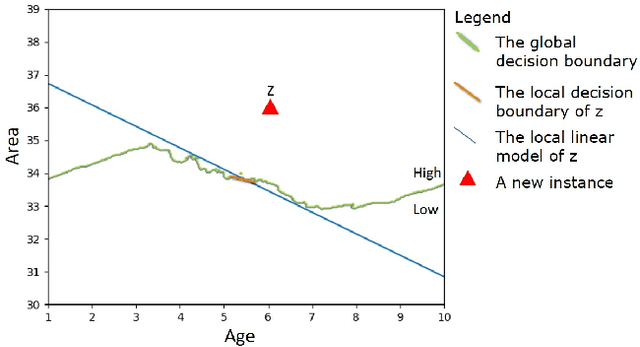
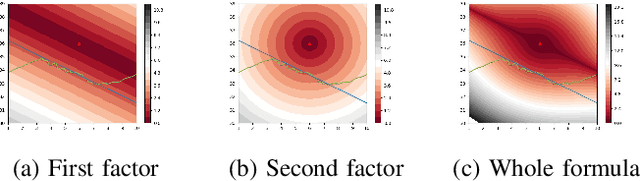
As machine learning models become more accurate, they typically become more complex and uninterpretable by humans. The black-box character of these models holds back its acceptance in practice, especially in high-risk domains where the consequences of failure could be catastrophic such as health-care or defense. Providing understandable and useful explanations behind ML models or predictions can increase the trust of the user. Example-based reasoning, which entails leveraging previous experience with analogous tasks to make a decision, is a well known strategy for problem solving and justification. This work presents a new explanation extraction method called LEAFAGE, for a prediction made by any black-box ML model. The explanation consists of the visualization of similar examples from the training set and the importance of each feature. Moreover, these explanations are contrastive which aims to take the expectations of the user into account. LEAFAGE is evaluated in terms of fidelity to the underlying black-box model and usefulness to the user. The results showed that LEAFAGE performs overall better than the current state-of-the-art method LIME in terms of fidelity, on ML models with non-linear decision boundary. A user-study was conducted which focused on revealing the differences between example-based and feature importance-based explanations. It showed that example-based explanations performed significantly better than feature importance-based explanation, in terms of perceived transparency, information sufficiency, competence and confidence. Counter-intuitively, when the gained knowledge of the participants was tested, it showed that they learned less about the black-box model after seeing a feature importance-based explanation than seeing no explanation at all. The participants found feature importance-based explanation vague and hard to generalize it to other instances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge