Evaluating and Improving Modern Variable and Revision Ordering Strategies in CSPs
Paper and Code
Aug 07, 2010
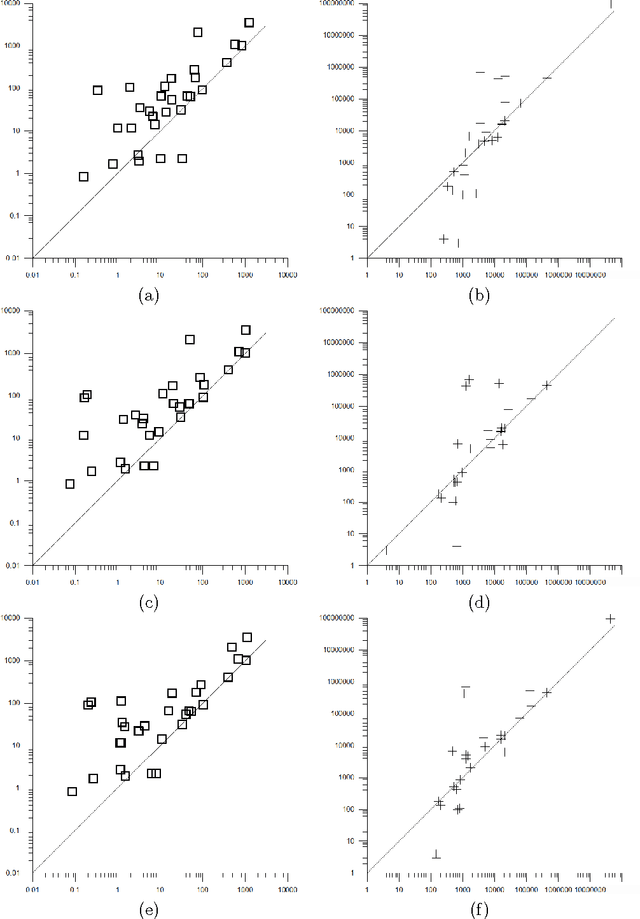
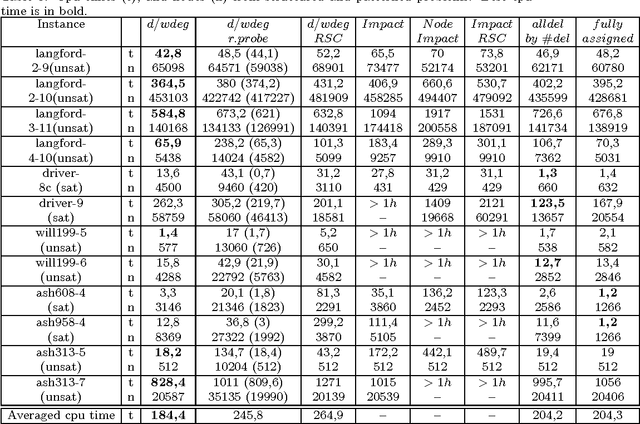
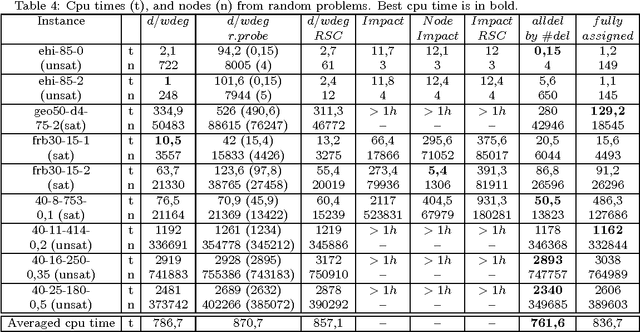
A key factor that can dramatically reduce the search space during constraint solving is the criterion under which the variable to be instantiated next is selected. For this purpose numerous heuristics have been proposed. Some of the best of such heuristics exploit information about failures gathered throughout search and recorded in the form of constraint weights, while others measure the importance of variable assignments in reducing the search space. In this work we experimentally evaluate the most recent and powerful variable ordering heuristics, and new variants of them, over a wide range of benchmarks. Results demonstrate that heuristics based on failures are in general more efficient. Based on this, we then derive new revision ordering heuristics that exploit recorded failures to efficiently order the propagation list when arc consistency is maintained during search. Interestingly, in addition to reducing the number of constraint checks and list operations, these heuristics are also able to cut down the size of the explored search tree.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge