Estimating the Brittleness of AI: Safety Integrity Levels and the Need for Testing Out-Of-Distribution Performance
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2020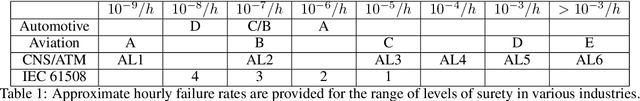

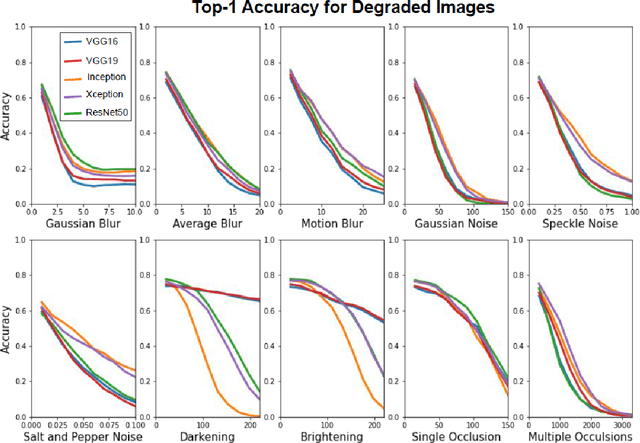
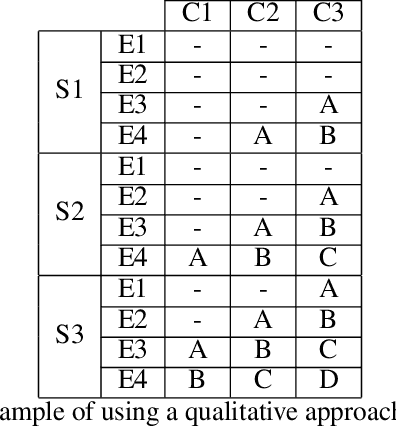
Test, Evaluation, Verification, and Validation (TEVV) for Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a challenge that threatens to limit the economic and societal rewards that AI researchers have devoted themselves to producing. A central task of TEVV for AI is estimating brittleness, where brittleness implies that the system functions well within some bounds and poorly outside of those bounds. This paper argues that neither of those criteria are certain of Deep Neural Networks. First, highly touted AI successes (eg. image classification and speech recognition) are orders of magnitude more failure-prone than are typically certified in critical systems even within design bounds (perfectly in-distribution sampling). Second, performance falls off only gradually as inputs become further Out-Of-Distribution (OOD). Enhanced emphasis is needed on designing systems that are resilient despite failure-prone AI components as well as on evaluating and improving OOD performance in order to get AI to where it can clear the challenging hurdles of TEVV and certification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge