Estimating Stochastic Poisson Intensities Using Deep Latent Models
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2020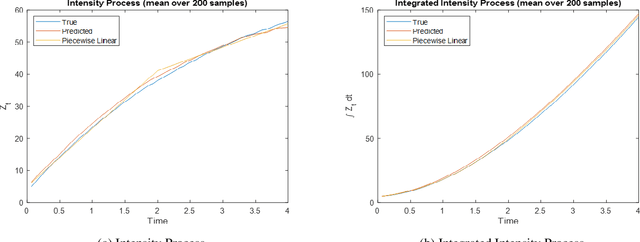
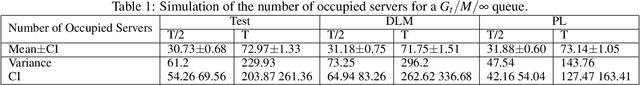
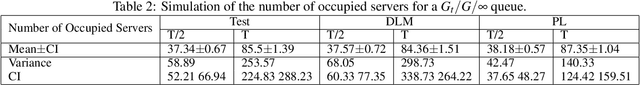
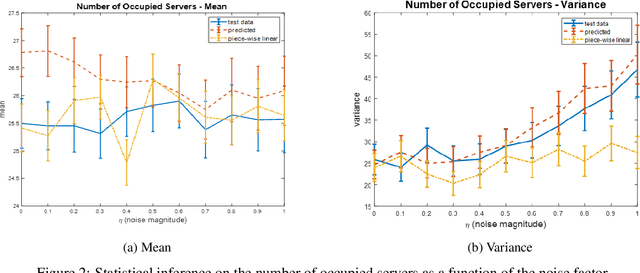
We present methodology for estimating the stochastic intensity of a doubly stochastic Poisson process. Statistical and theoretical analyses of traffic traces show that these processes are appropriate models of high intensity traffic arriving at an array of service systems. The statistical estimation of the underlying latent stochastic intensity process driving the traffic model involves a rather complicated nonlinear filtering problem. We develop a novel simulation methodology, using deep neural networks to approximate the path measures induced by the stochastic intensity process, for solving this nonlinear filtering problem. Our simulation studies demonstrate that the method is quite accurate on both in-sample estimation and on an out-of-sample performance prediction task for an infinite server queue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge