Equine radiograph classification using deep convolutional neural networks
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2022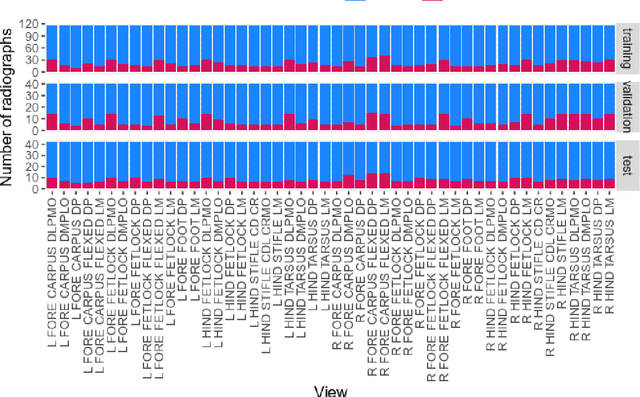
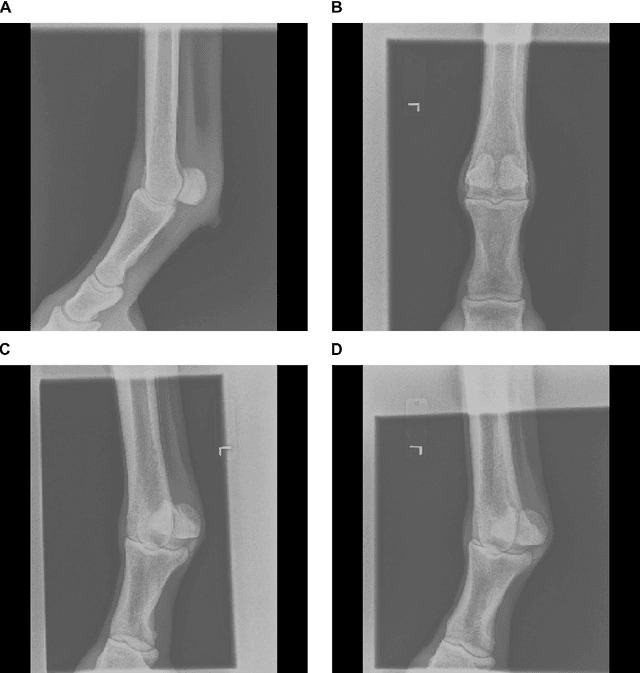
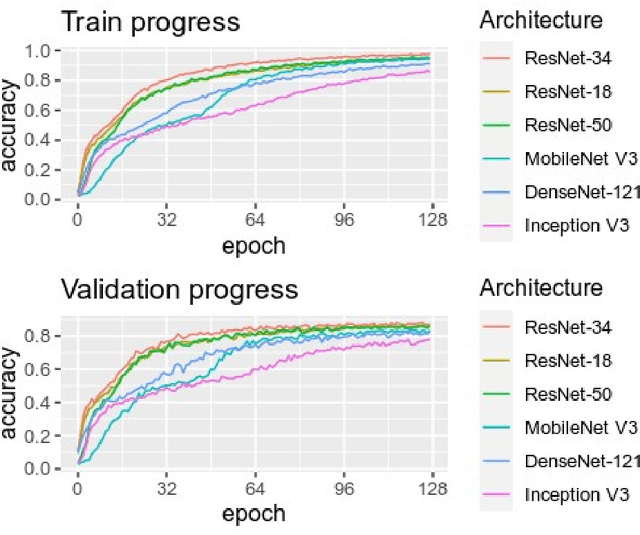
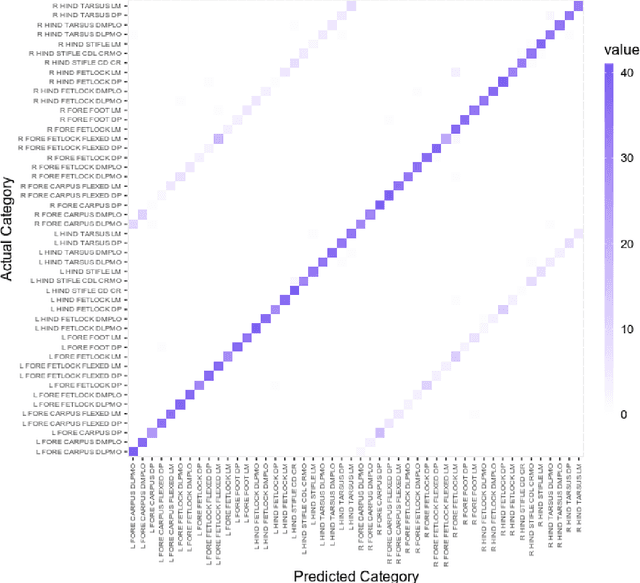
Purpose: To assess the capability of deep convolutional neural networks to classify anatomical location and projection from a series of 48 standard views of racehorse limbs. Materials and Methods: 9504 equine pre-import radiographs were used to train, validate, and test six deep learning architectures available as part of the open source machine learning framework PyTorch. Results: ResNet-34 achieved a top-1 accuracy of 0.8408 and the majority (88%) of misclassification was because of wrong laterality. Class activation maps indicated that joint morphology drove the model decision. Conclusion: Deep convolutional neural networks are capable of classifying equine pre-import radiographs into the 48 standard views including moderate discrimination of laterality independent of side marker presence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge