Ensemble Learning for Microbubble Localization in Super-Resolution Ultrasound
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2024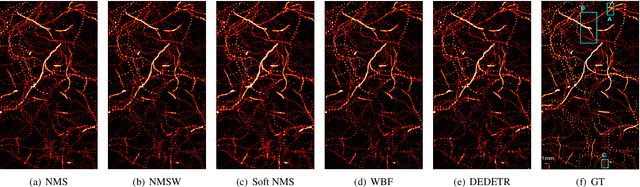
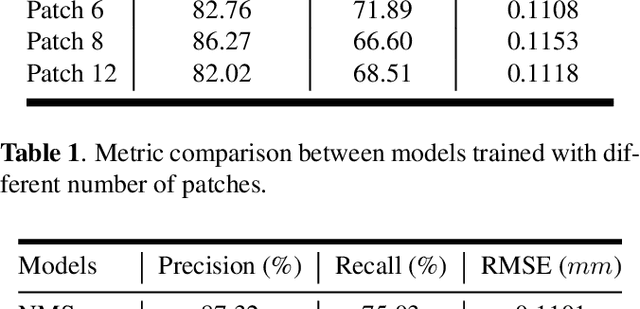
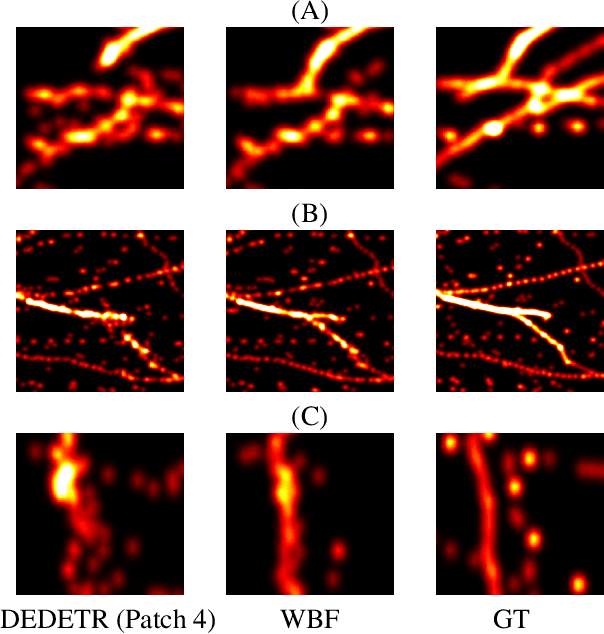

Super-resolution ultrasound (SR-US) is a powerful imaging technique for capturing microvasculature and blood flow at high spatial resolution. However, accurate microbubble (MB) localization remains a key challenge, as errors in localization can propagate through subsequent stages of the super-resolution process, affecting overall performance. In this paper, we explore the potential of ensemble learning techniques to enhance MB localization by increasing detection sensitivity and reducing false positives. Our study evaluates the effectiveness of ensemble methods on both in vivo and simulated outputs of a Deformable DEtection TRansformer (Deformable DETR) network. As a result of our study, we are able to demonstrate the advantages of these ensemble approaches by showing improved precision and recall in MB detection and offering insights into their application in SR-US.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge