Ensemble-based kernel learning for a class of data assimilation problems with imperfect forward simulators
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2019
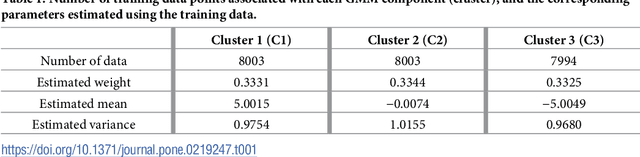
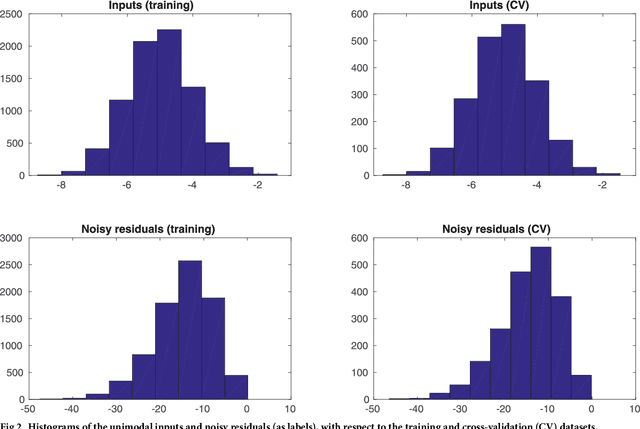
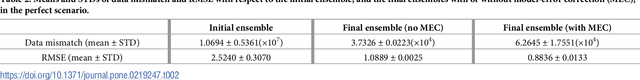
Simulator imperfection, often known as model error, is ubiquitous in practical data assimilation problems. Despite the enormous efforts dedicated to addressing this problem, properly handling simulator imperfection in data assimilation remains to be a challenging task. In this work, we propose an approach to dealing with simulator imperfection from a point of view of functional approximation that can be implemented through a certain machine learning method, such as kernel-based learning adopted in the current work. To this end, we start from considering a class of supervised learning problems, and then identify similarities between supervised learning and variational data assimilation. These similarities found the basis for us to develop an ensemble-based learning framework to tackle supervised learning problems, while achieving various advantages of ensemble-based methods over the variational ones. After establishing the ensemble-based learning framework, we proceed to investigate the integration of ensemble-based learning into an ensemble-based data assimilation framework to handle simulator imperfection. In the course of our investigations, we also develop a strategy to tackle the issue of multi-modality in supervised-learning problems, and transfer this strategy to data assimilation problems to help improve assimilation performance. For demonstration, we apply the ensemble-based learning framework and the integrated, ensemble-based data assimilation framework to a supervised learning problem and a data assimilation problem with an imperfect forward simulator, respectively. The experiment results indicate that both frameworks achieve good performance in relevant case studies, and that functional approximation through machine learning may serve as a viable way to account for simulator imperfection in data assimilation problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge