Enhancing Speaker Diarization with Large Language Models: A Contextual Beam Search Approach
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2023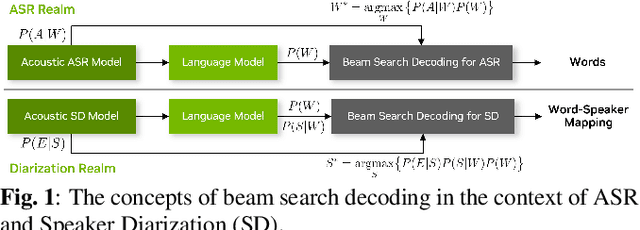
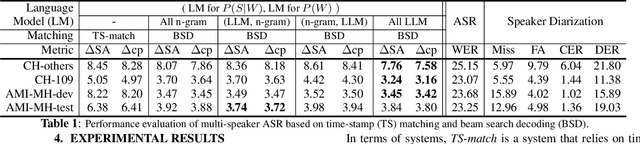
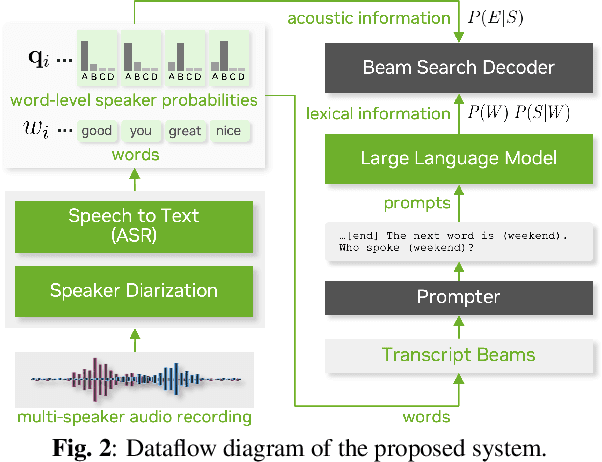
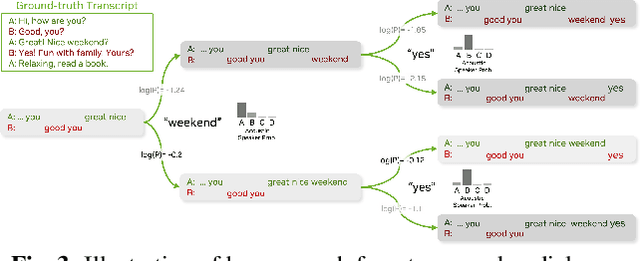
Large language models (LLMs) have shown great promise for capturing contextual information in natural language processing tasks. We propose a novel approach to speaker diarization that incorporates the prowess of LLMs to exploit contextual cues in human dialogues. Our method builds upon an acoustic-based speaker diarization system by adding lexical information from an LLM in the inference stage. We model the multi-modal decoding process probabilistically and perform joint acoustic and lexical beam search to incorporate cues from both modalities: audio and text. Our experiments demonstrate that infusing lexical knowledge from the LLM into an acoustics-only diarization system improves overall speaker-attributed word error rate (SA-WER). The experimental results show that LLMs can provide complementary information to acoustic models for the speaker diarization task via proposed beam search decoding approach showing up to 39.8% relative delta-SA-WER improvement from the baseline system. Thus, we substantiate that the proposed technique is able to exploit contextual information that is inaccessible to acoustics-only systems which is represented by speaker embeddings. In addition, these findings point to the potential of using LLMs to improve speaker diarization and other speech processing tasks by capturing semantic and contextual cues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge