Enhancing Identification of Causal Effects by Pruning
Paper and Code
Jun 19, 2018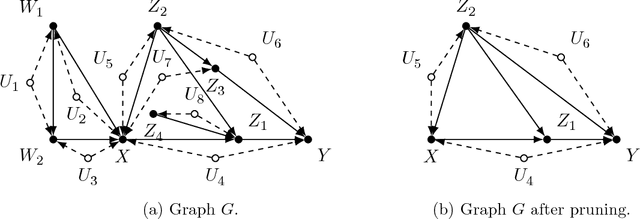
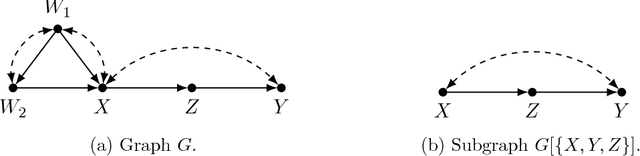
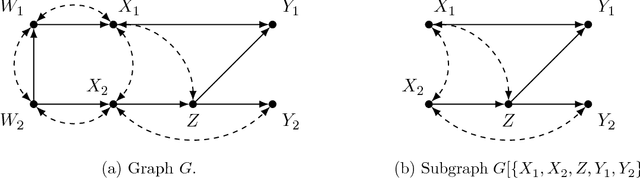
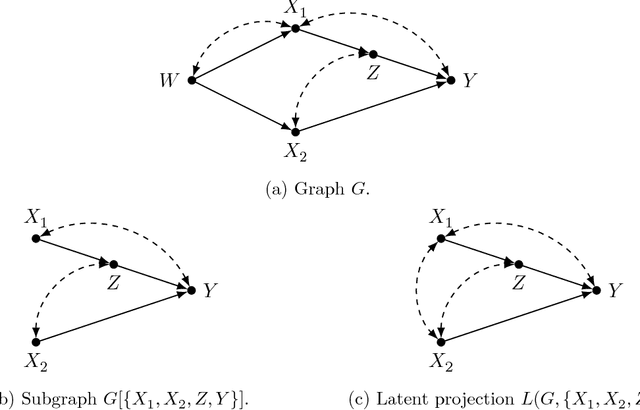
Causal models communicate our assumptions about causes and effects in real-world phe- nomena. Often the interest lies in the identification of the effect of an action which means deriving an expression from the observed probability distribution for the interventional distribution resulting from the action. In many cases an identifiability algorithm may return a complicated expression that contains variables that are in fact unnecessary. In practice this can lead to additional computational burden and increased bias or inefficiency of estimates when dealing with measurement error or missing data. We present graphical criteria to detect variables which are redundant in identifying causal effects. We also provide an improved version of a well-known identifiability algorithm that implements these criteria.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge