Enhancing Carbon Emission Reduction Strategies using OCO and ICOS data
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2024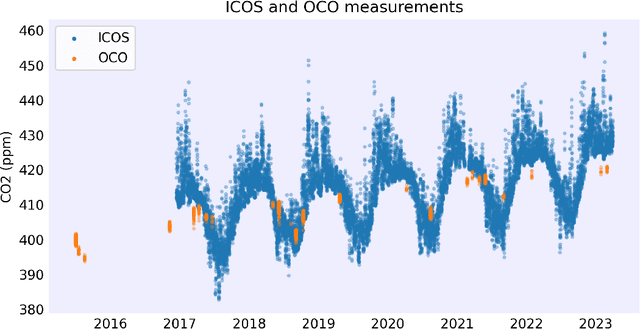
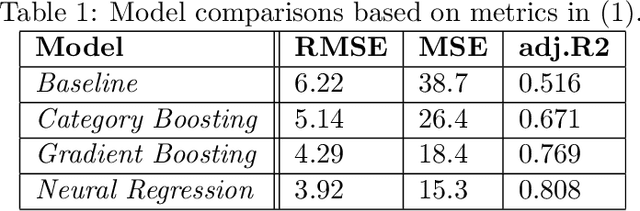
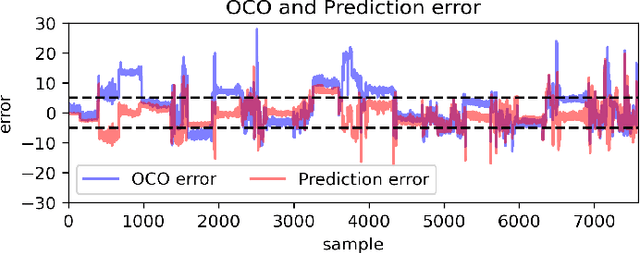
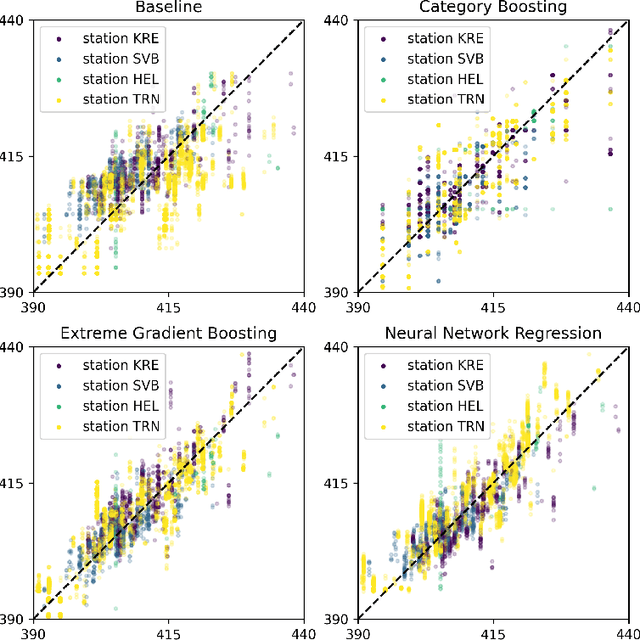
We propose a methodology to enhance local CO2 monitoring by integrating satellite data from the Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO-2 and OCO-3) with ground level observations from the Integrated Carbon Observation System (ICOS) and weather data from the ECMWF Reanalysis v5 (ERA5). Unlike traditional methods that downsample national data, our approach uses multimodal data fusion for high-resolution CO2 estimations. We employ weighted K-nearest neighbor (KNN) interpolation with machine learning models to predict ground level CO2 from satellite measurements, achieving a Root Mean Squared Error of 3.92 ppm. Our results show the effectiveness of integrating diverse data sources in capturing local emission patterns, highlighting the value of high-resolution atmospheric transport models. The developed model improves the granularity of CO2 monitoring, providing precise insights for targeted carbon mitigation strategies, and represents a novel application of neural networks and KNN in environmental monitoring, adaptable to various regions and temporal scales.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge