End-to-End Uplink Performance Analysis of Satellite-Based IoT Networks: A Stochastic Geometry Approach
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2024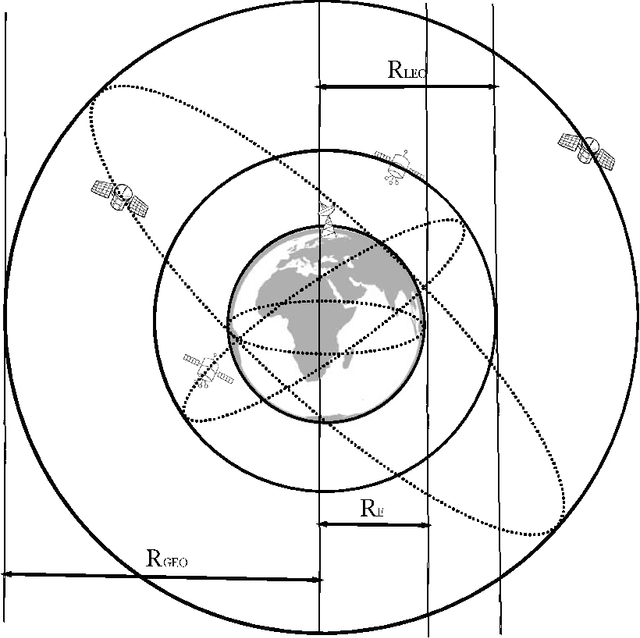
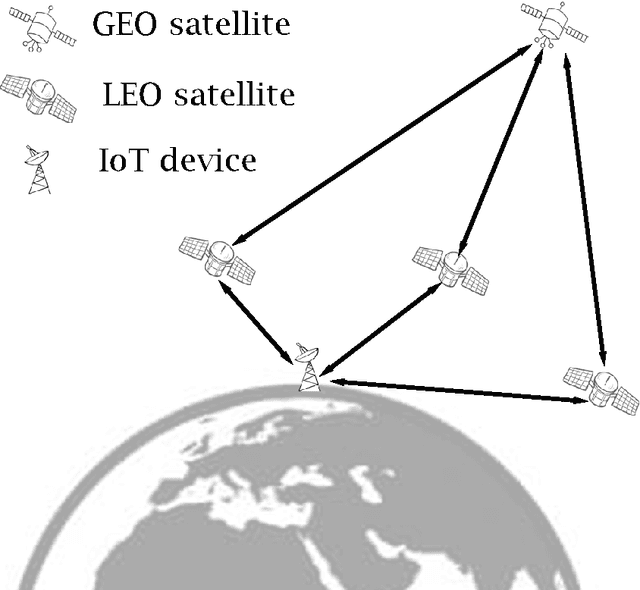
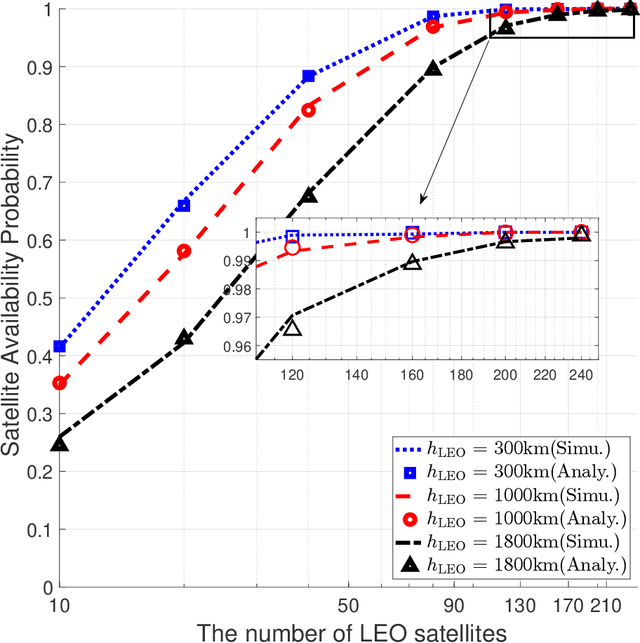
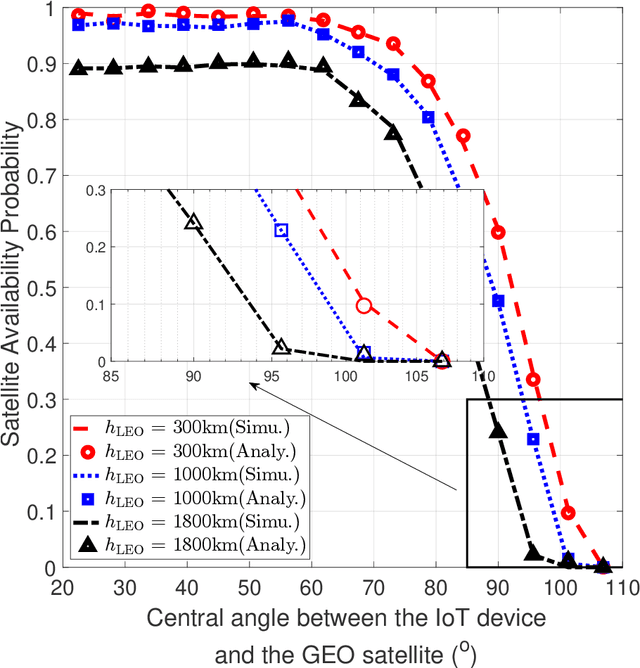
With the deployment of satellite constellations, Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices in remote areas have gained access to low-cost network connectivity. In this paper, we investigate the performance of IoT devices connecting in up-link through low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites to geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO) links. We model the dynamic LEO satellite constellation using the stochastic geometry method and provide an analysis of end-to-end availability with low-complexity and coverage performance estimates for the mentioned link. Based on the analytical expressions derived in this research, we make a sound investigation on the impact of constellation configuration, transmission power, and the relative positions of IoT devices and GEO satellites on end-to-end performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge