Empirical Evaluation of A New Approach to Simplifying Long Short-term Memory
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2016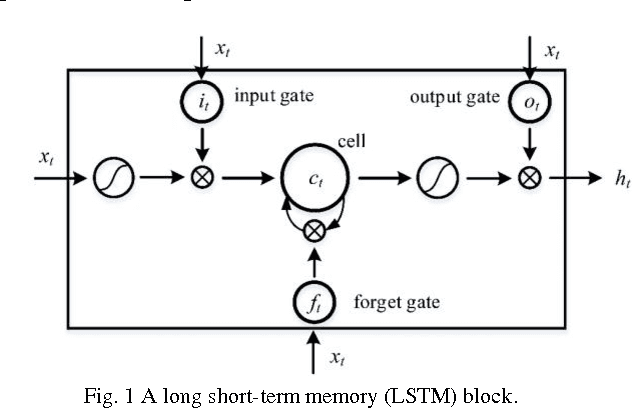
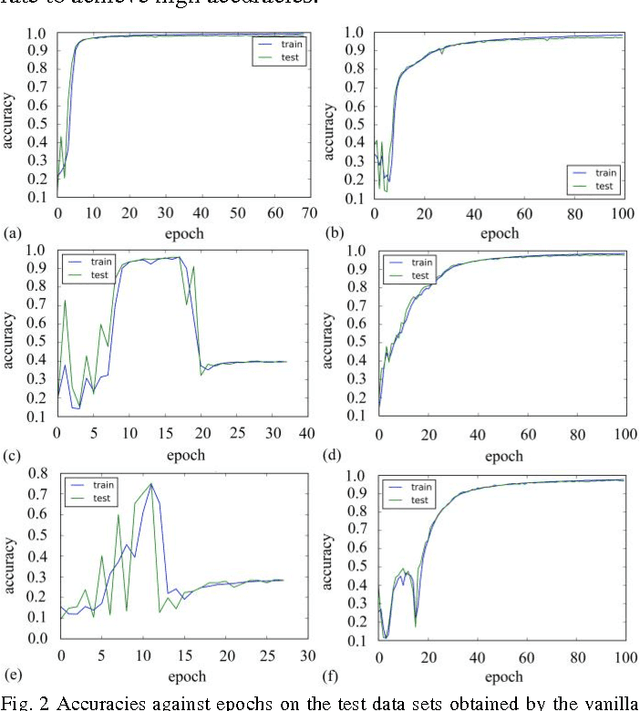
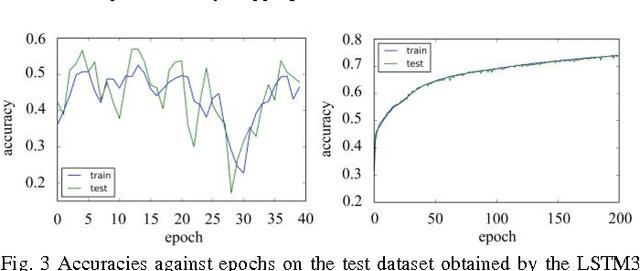
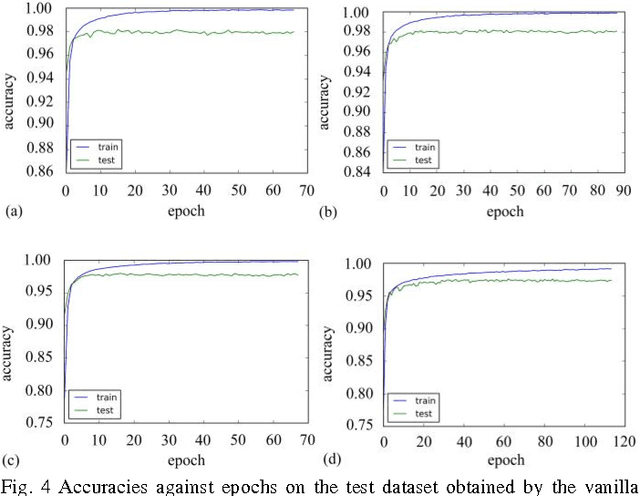
The standard LSTM, although it succeeds in the modeling long-range dependences, suffers from a highly complex structure that can be simplified through modifications to its gate units. This paper was to perform an empirical comparison between the standard LSTM and three new simplified variants that were obtained by eliminating input signal, bias and hidden unit signal from individual gates, on the tasks of modeling two sequence datasets. The experiments show that the three variants, with reduced parameters, can achieve comparable performance with the standard LSTM. Due attention should be paid to turning the learning rate to achieve high accuracies
* 5 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge