EmbPred30: Assessing 30-days Readmission for Diabetic Patients using Categorical Embeddings
Paper and Code
Feb 25, 2020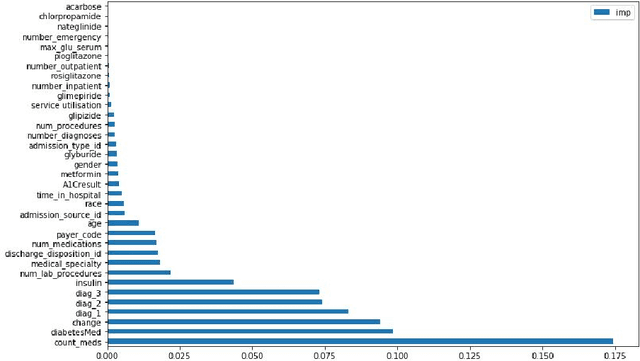
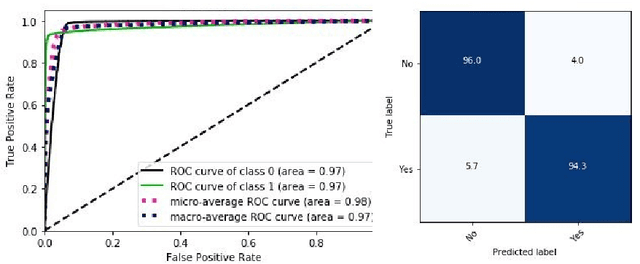
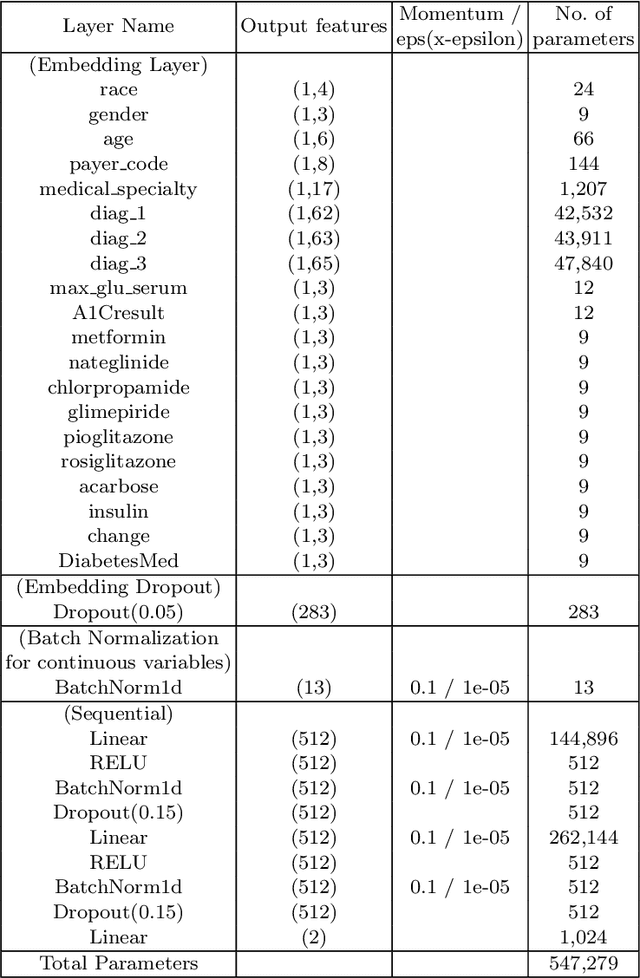
Hospital readmission is a crucial healthcare quality measure that helps in determining the level of quality of care that a hospital offers to a patient and has proven to be immensely expensive. It is estimated that more than $25 billion are spent yearly due to readmission of diabetic patients in the USA. This paper benchmarks existing models and proposes a new embedding based state-of-the-art deep neural network(DNN). The model can identify whether a hospitalized diabetic patient will be readmitted within 30 days or not with an accuracy of 95.2% and Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics(AUROC) of 97.4% on data collected from 130 US hospitals between 1999-2008. The results are encouraging with patients having changes in medication while admitted having a high chance of getting readmitted. Identifying prospective patients for readmission could help the hospital systems in improving their inpatient care, thereby saving them from unnecessary expenditures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge