EM-based Solutions for Covariance Structure Detection and Classification in Polarimetric SAR Images
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2021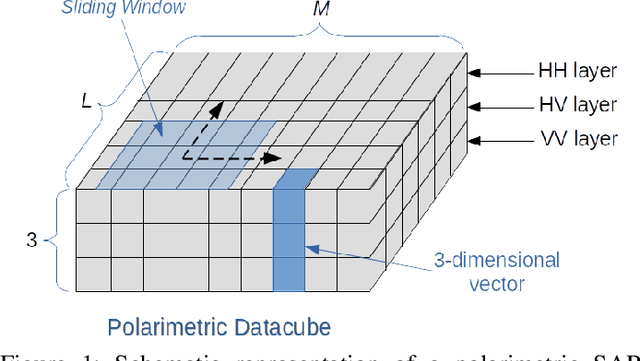
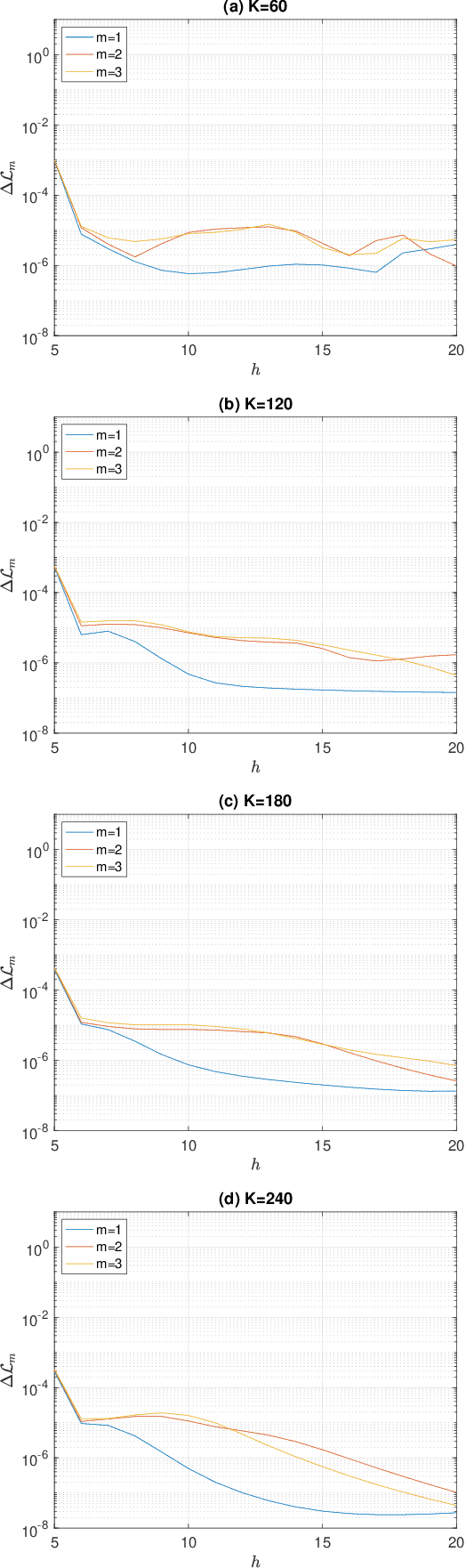
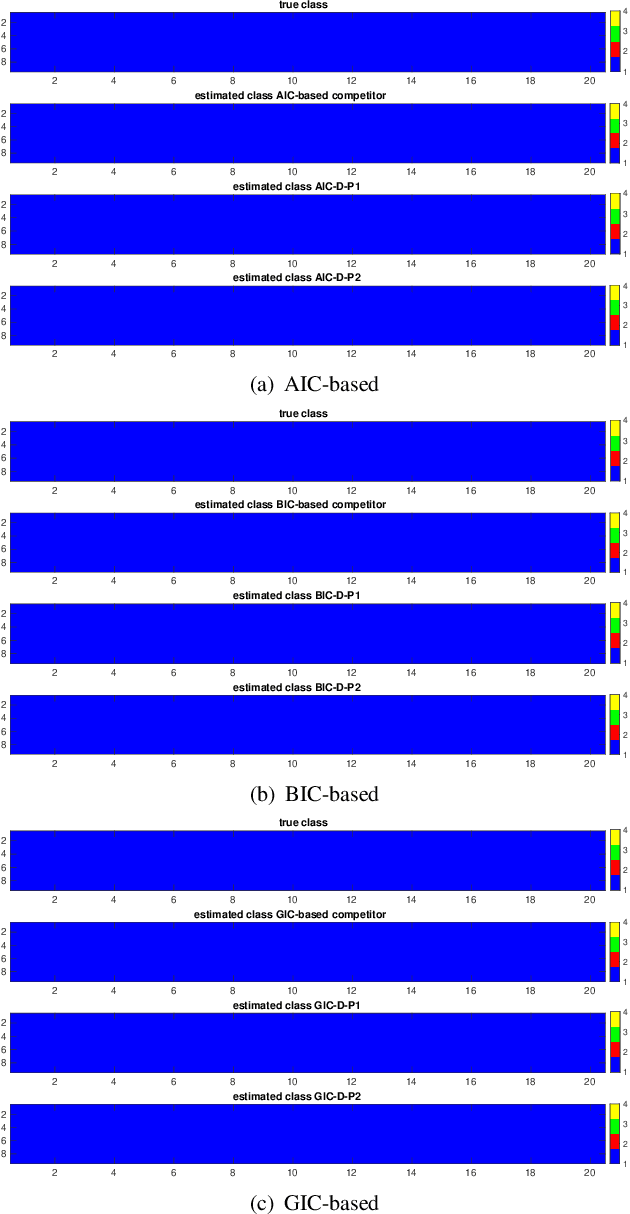
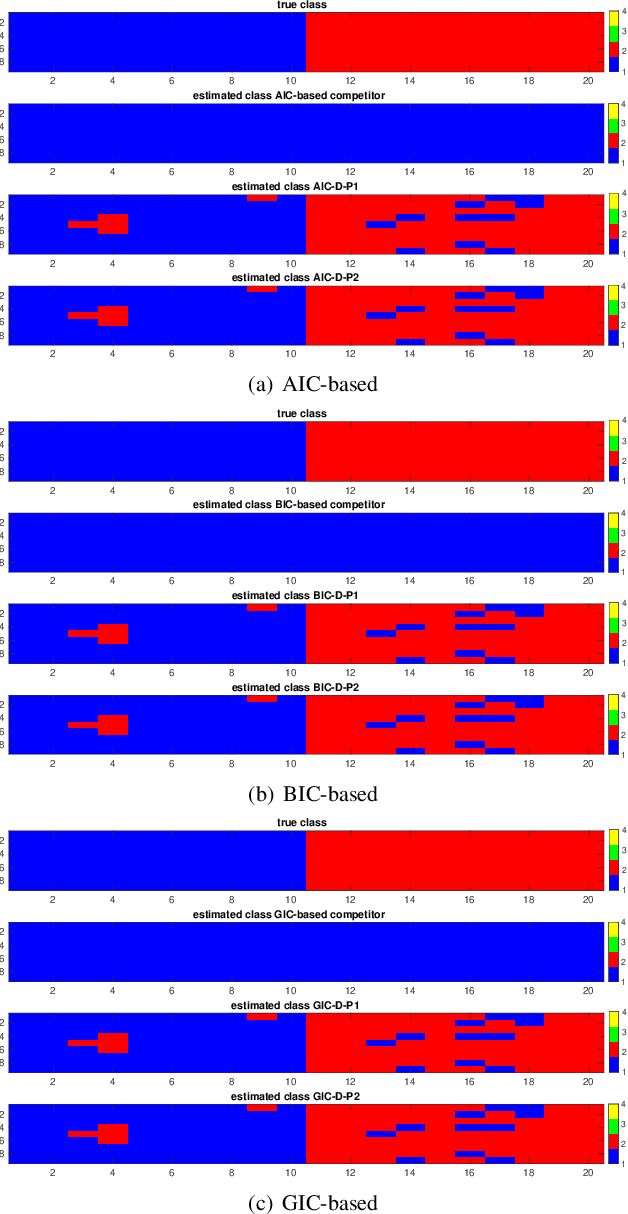
This paper addresses the challenge of classifying polarimetric SAR images by leveraging the peculiar characteristics of the polarimetric covariance matrix (PCM). To this end, a general framework to solve a multiple hypothesis test is introduced with the aim to detect and classify contextual spatial variations in polarimetric SAR images. Specifically, under the null hypothesis, only an unknown structure is assumed for data belonging to a 2-dimensional spatial sliding window, whereas under each alternative hypothesis, data are partitioned into subsets sharing different structures. The problem of partition estimation is solved by resorting to hidden random variables representative of covariance structure classes and the expectation-maximization algorithm. The effectiveness of the proposed detection strategies is demonstrated on both simulated and real polarimetric SAR data also in comparison with existing classification algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge