Efficient Dodgson-Score Calculation Using Heuristics and Parallel Computing
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2016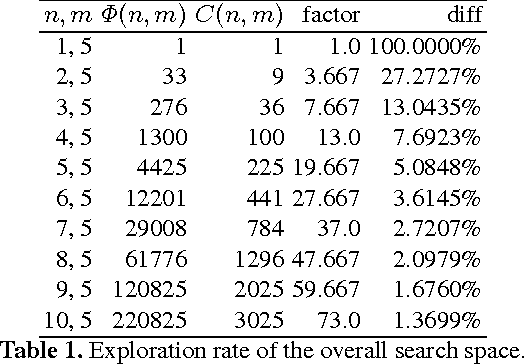
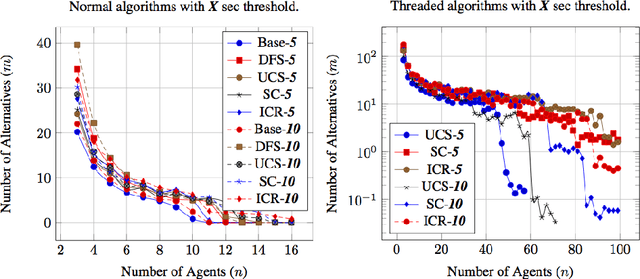
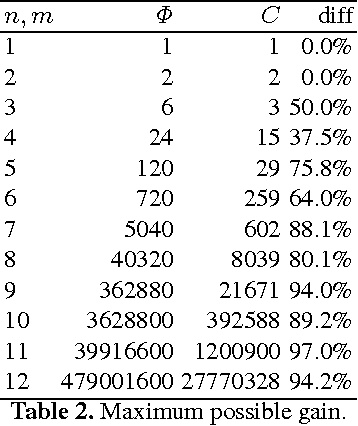
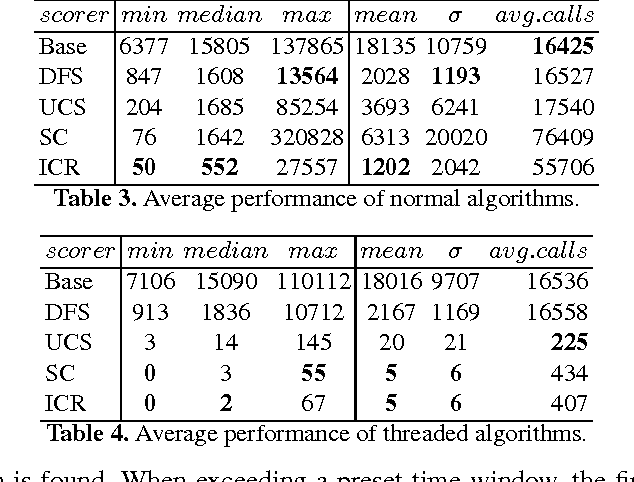
Conflict of interest is the permanent companion of any population of agents (computational or biological). For that reason, the ability to compromise is of paramount importance, making voting a key element of societal mechanisms. One of the voting procedures most often discussed in the literature and, due to its intuitiveness, also conceptually quite appealing is Charles Dodgson's scoring rule, basically using the respective closeness to being a Condorcet winner for evaluating competing alternatives. In this paper, we offer insights on the practical limits of algorithms computing the exact Dodgson scores from a number of votes. While the problem itself is theoretically intractable, this work proposes and analyses five different solutions which try distinct approaches to practically solve the issue in an effective manner. Additionally, three of the discussed procedures can be run in parallel which has the potential of drastically reducing the problem size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge