Efficient Coding Approach Towards Non-Linear Spectro-Temporal Receptive Fields
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2021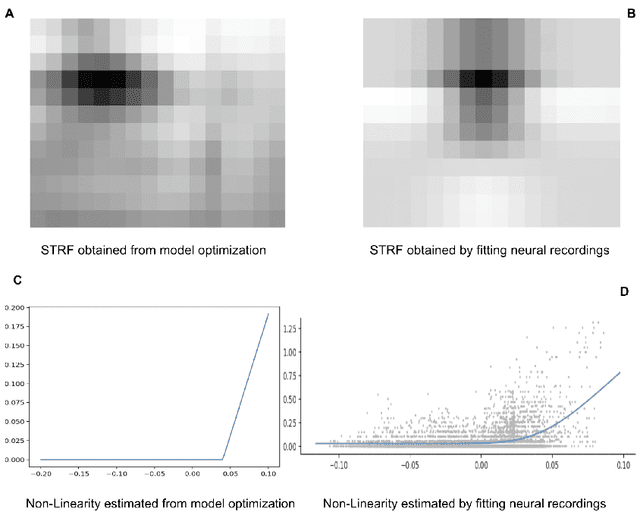
Linear Non-Linear(LN) models are widely used to characterize the receptive fields of early-stage auditory processing. We apply the principle of efficient coding to the LN model of Spectro-Temporal Receptive Fields(STRFs) of the neurons in primary auditory cortex. The Efficient Coding Principle has been previously used to understand early visual receptive fields and linear STRFs in auditory processing. Efficient coding is realized by jointly optimizing the mutual information between stimuli and neural responses subjected to the metabolic cost of firing spikes. We compare the predictions of the efficient coding principle with the physiological observations, which match qualitatively under realistic conditions of noise in stimuli and the spike generation process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge