Efficient Area-based and Speaker-Agnostic Source Separation
Paper and Code
Aug 19, 2024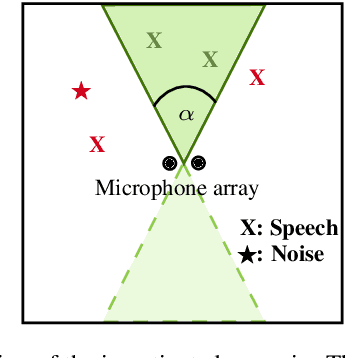
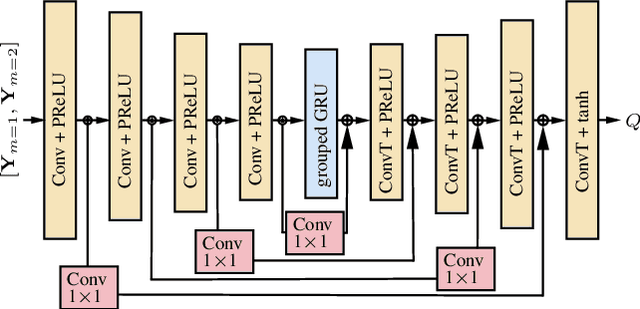
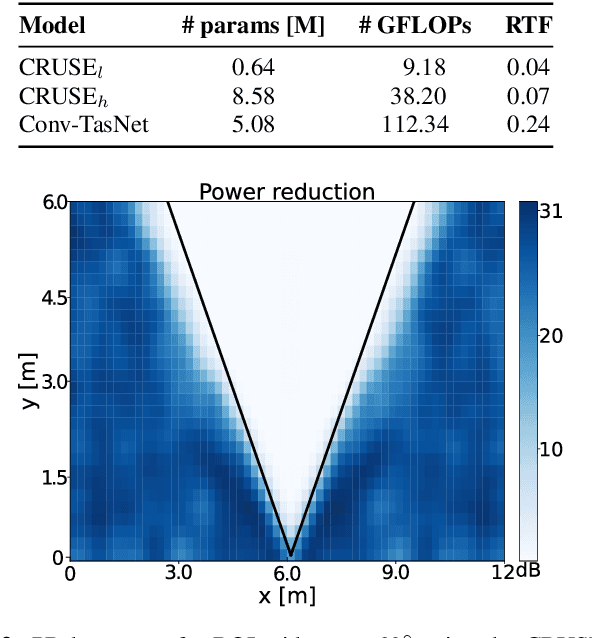
This paper introduces an area-based source separation method designed for virtual meeting scenarios. The aim is to preserve speech signals from an unspecified number of sources within a defined spatial area in front of a linear microphone array, while suppressing all other sounds. Therefore, we employ an efficient neural network architecture adapted for multi-channel input to encompass the predefined target area. To evaluate the approach, training data and specific test scenarios including multiple target and interfering speakers, as well as background noise are simulated. All models are rated according to DNSMOS and scale-invariant signal-to-distortion ratio. Our experiments show that the proposed method separates speech from multiple speakers within the target area well, besides being of very low complexity, intended for real-time processing. In addition, a power reduction heatmap is used to demonstrate the networks' ability to identify sources located within the target area. We put our approach in context with a well-established baseline for speaker-speaker separation and discuss its strengths and challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge