Effects of seat back height and posture on 3D vibration transmission to pelvis, trunk and head
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2022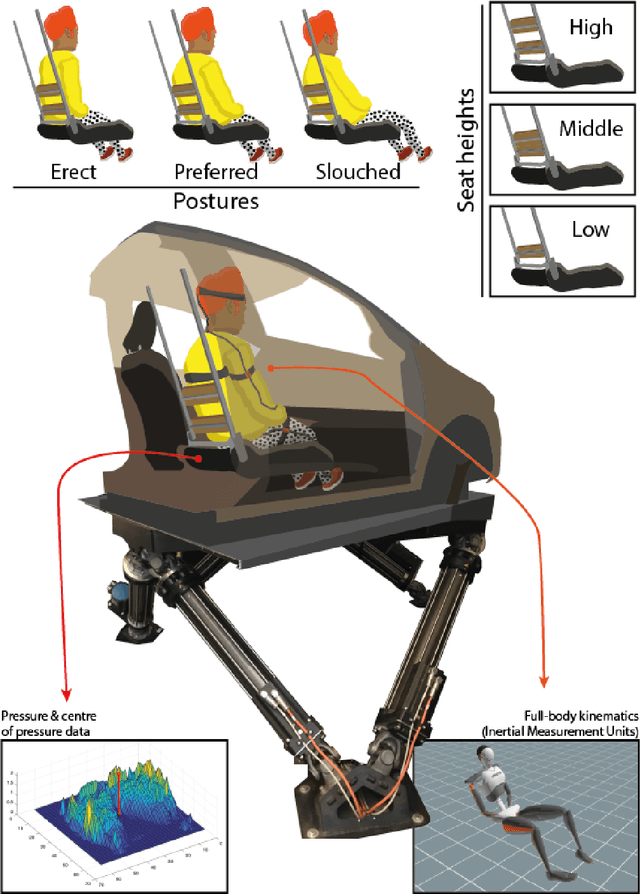
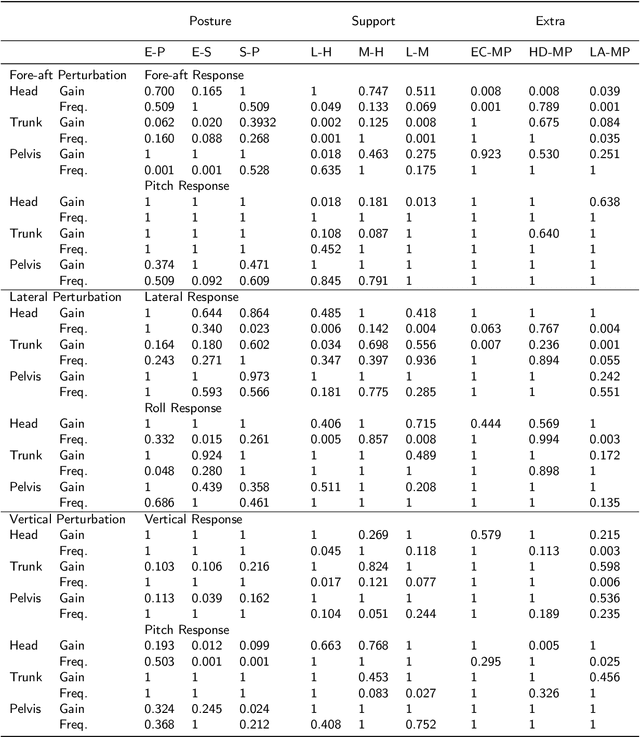
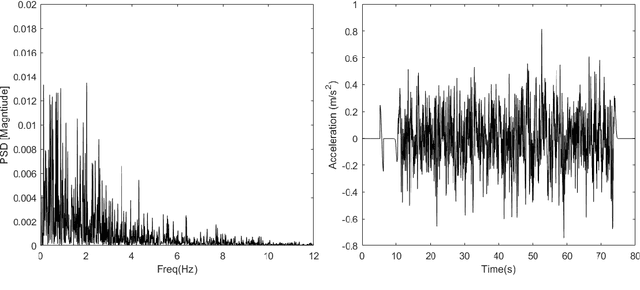
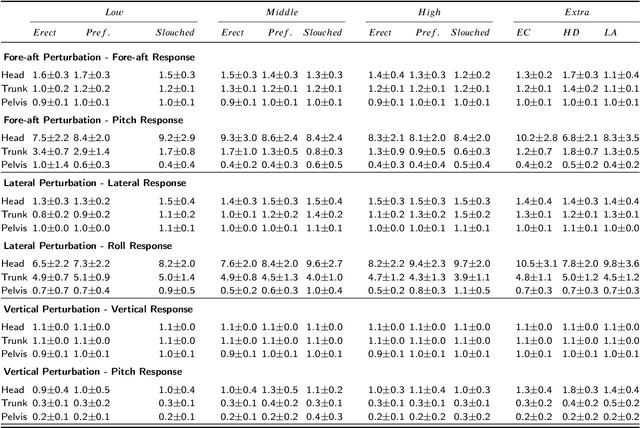
Vibration transmission is essential in the design of comfortable vehicle seats but knowledge is lacking on 3D trunk and head motion and the role of seat back and posture. We hypothesized that head motion is reduced when participants upper back is unsupported, as this stimulates active postural control. We developed an experimental methodology to evaluate 3D vibration transmission from compliant seats to the human body. Wide-band (0.1-12 Hz) motion stimuli were applied in fore-aft, lateral and vertical direction to evaluate the translational and rotational body response in pelvis, trunk and head. A standard car seat was equipped with a configurable and compliant back support to test 3 support heights and 3 sitting postures (erect, slouched, and preferred) where we also tested head down looking at a smartphone. Seat back support height and sitting posture substantially affected vibration transmission and affected low-frequency responses in particular for body segment rotation. According to our hypothesis a low support height proved beneficial in reducing head motion. Relevance to industry: Our methodology effectively evaluates 3D wide-band vibration transmission from compliant seats to the human body. The lowest back support height reduced head motion but was perceived as least comfortable. This calls for seat designs which support but do not so much constrain the upper back. The head down posture enlarged head motion, pleading for computer system integration allowing heads up postures in future automated cars. The biomechanical data will serve to validate human models supporting the design of comfortable (automated) vehicles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge