Effective extractive summarization using frequency-filtered entity relationship graphs
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2018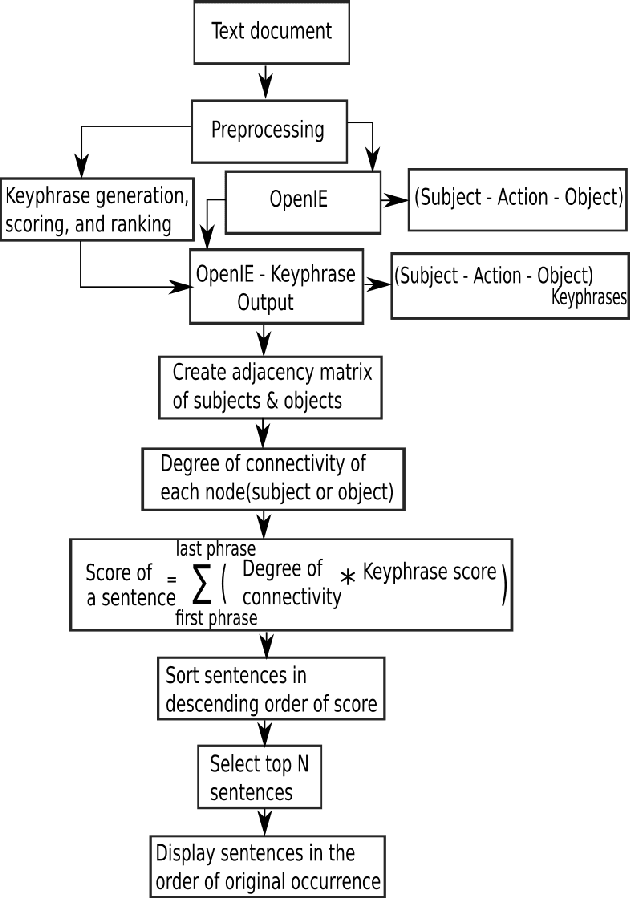
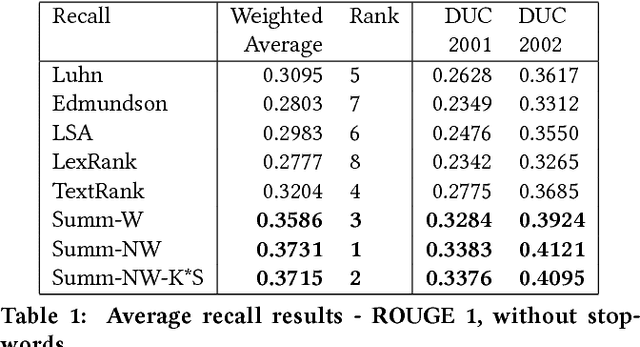
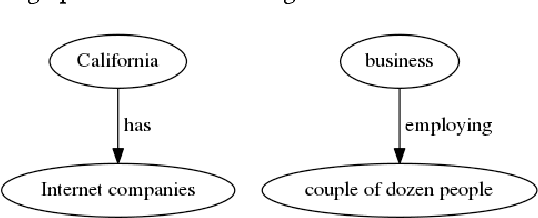
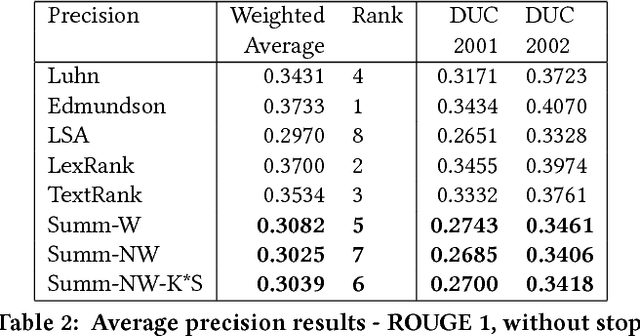
Word frequency-based methods for extractive summarization are easy to implement and yield reasonable results across languages. However, they have significant limitations - they ignore the role of context, they offer uneven coverage of topics in a document, and sometimes are disjointed and hard to read. We use a simple premise from linguistic typology - that English sentences are complete descriptors of potential interactions between entities, usually in the order subject-verb-object - to address a subset of these difficulties. We have developed a hybrid model of extractive summarization that combines word-frequency based keyword identification with information from automatically generated entity relationship graphs to select sentences for summaries. Comparative evaluation with word-frequency and topic word-based methods shows that the proposed method is competitive by conventional ROUGE standards, and yields moderately more informative summaries on average, as assessed by a large panel (N=94) of human raters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge