Effect of the regularization hyperparameter on deep learning-based segmentation in LGE-MRI
Paper and Code
Dec 15, 2020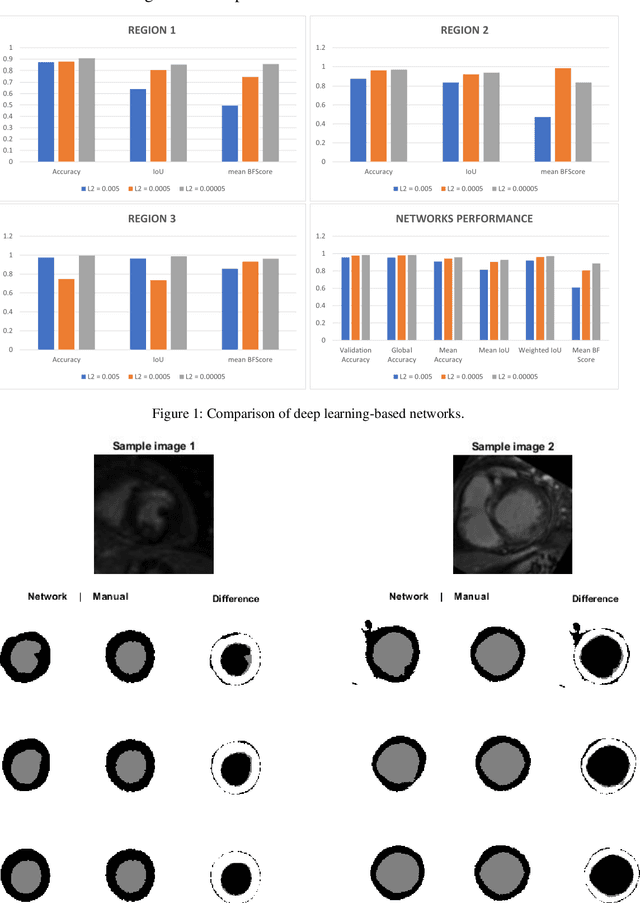
In this work, the author aims at demonstrating the extent to which the arbitrary selection of the L2 regularization hyperparameter can affect the outcome of deep learning-based segmentation in LGE-MRI. Here, arbitrary L2 regularization values are used to create different deep learning-based segmentation networks. Also, the author adopts the manual adjustment or tunning, of other deep learning hyperparameters, to be done only when 10% of all epochs are reached before achieving the 90% validation accuracy. The experimental comparisons demonstrate that small L2 regularization values can lead to better segmentation of the myocardial boundaries.
* 5 pages, 2 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge