Effect of context in swipe gesture-based continuous authentication on smartphones
Paper and Code
May 28, 2019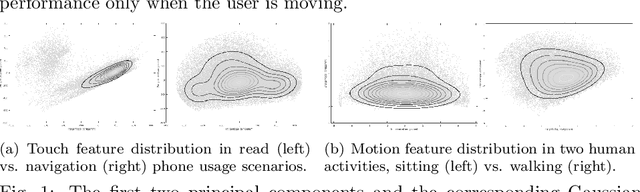
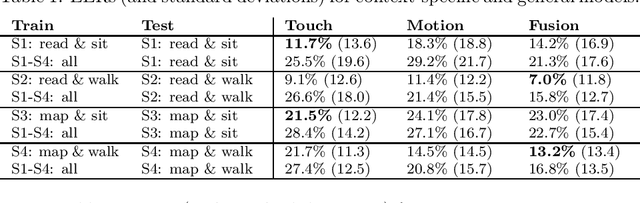
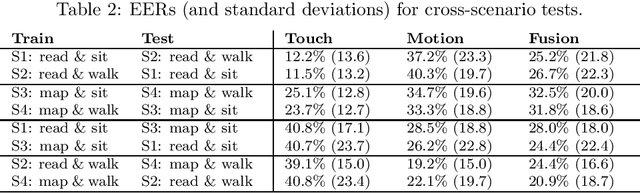
This work investigates how context should be taken into account when performing continuous authentication of a smartphone user based on touchscreen and accelerometer readings extracted from swipe gestures. The study is conducted on the publicly available HMOG dataset consisting of 100 study subjects performing pre-defined reading and navigation tasks while sitting and walking. It is shown that context-specific models are needed for different smartphone usage and human activity scenarios to minimize authentication error. Also, the experimental results suggests that utilization of phone movement improves swipe gesture-based verification performance only when the user is moving.
* European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational
Intelligence and Machine Learning (ESANN) 2018, pages 639-644
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge