EEG to fMRI Synthesis Benefits from Attentional Graphs of Electrode Relationships
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2022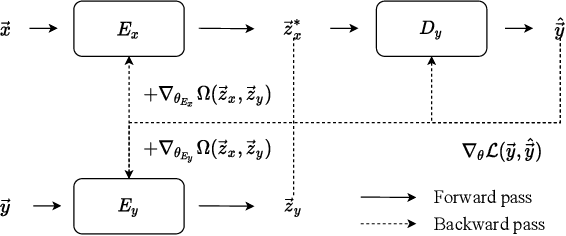
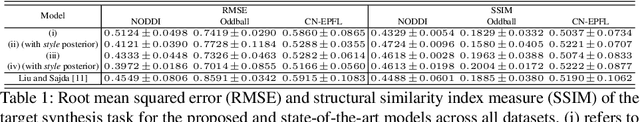
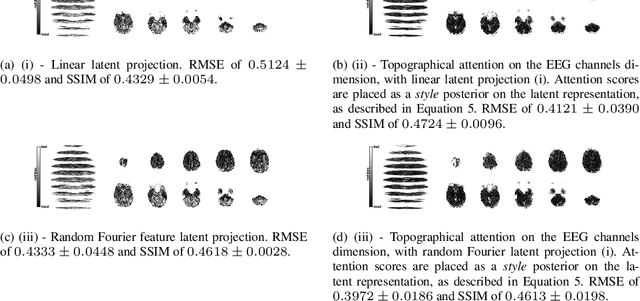
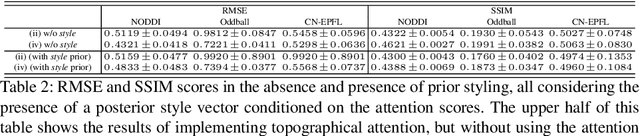
Topographical structures represent connections between entities and provide a comprehensive design of complex systems. Currently these structures are used to discover correlates of neuronal and haemodynamical activity. In this work, we incorporate them with neural processing techniques to perform regression, using electrophysiological activity to retrieve haemodynamics. To this end, we use Fourier features, attention mechanisms, shared space between modalities and incorporation of style in the latent representation. By combining these techniques, we propose several models that significantly outperform current state-of-the-art of this task in resting state and task-based recording settings. We report which EEG electrodes are the most relevant for the regression task and which relations impacted it the most. In addition, we observe that haemodynamic activity at the scalp, in contrast with sub-cortical regions, is relevant to the learned shared space. Overall, these results suggest that EEG electrode relationships are pivotal to retain information necessary for haemodynamical activity retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge