Echo-enabled Direction-of-Arrival and range estimation of a mobile source in Ambisonic domain
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2022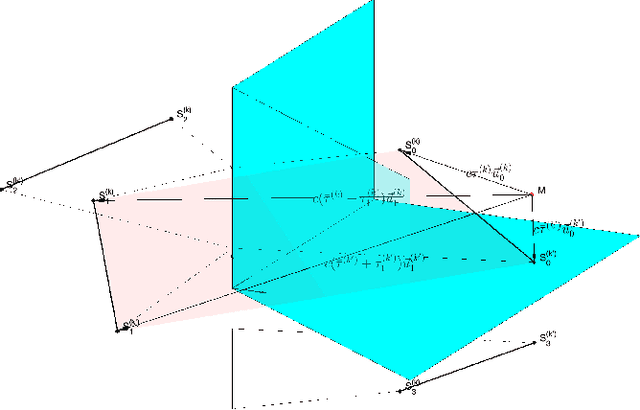
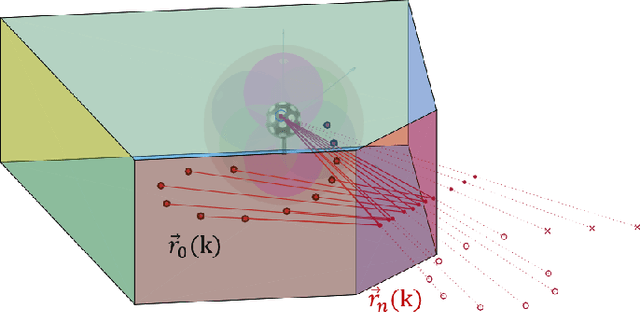
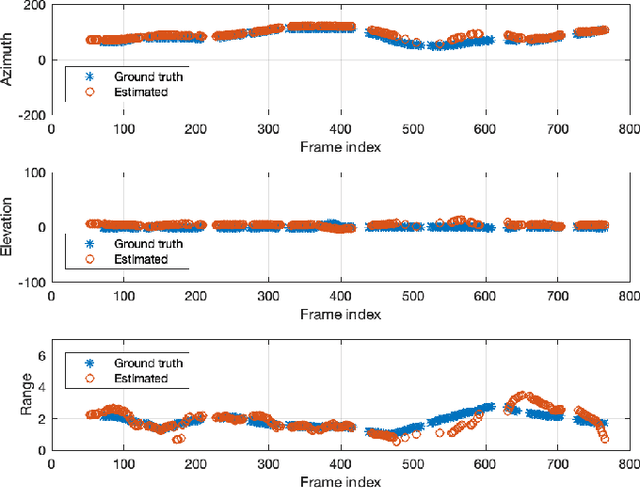
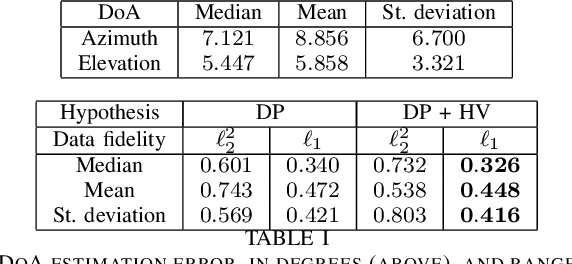
Range estimation of a far field sound source in a reverberant environment is known to be a notoriously difficult problem, hence most localization methods are only capable of estimating the source's Direction-of-Arrival (DoA). In an earlier work, we have demonstrated that, under certain restrictive acoustic conditions and given the orientation of a reflecting surface, one can exploit the dominant acoustic reflection to evaluate the DoA \emph{and} the distance to a static sound source in Ambisonic domain. In this article, we leverage the recently presented Generalized Time-domain Velocity Vector (GTVV) representation to estimate these quantities for a moving sound source without an a priori knowledge of reflectors' orientations. We show that the trajectories of a moving source and the corresponding reflections are spatially and temporally related, which can be used to infer the absolute delay of the propagating source signal and, therefore, approximate the microphone-to-source distance. Experiments on real sound data confirm the validity of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge