Dynamic Query Selection for Fast Visual Perceiver
Paper and Code
May 22, 2022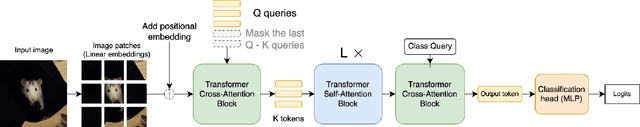
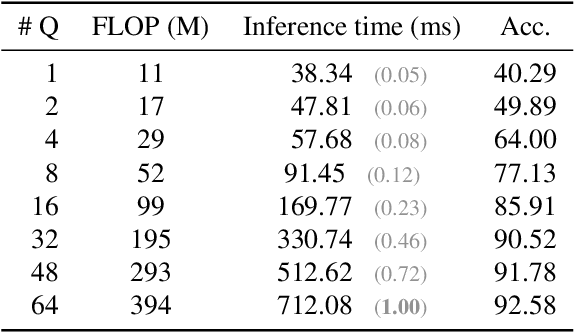
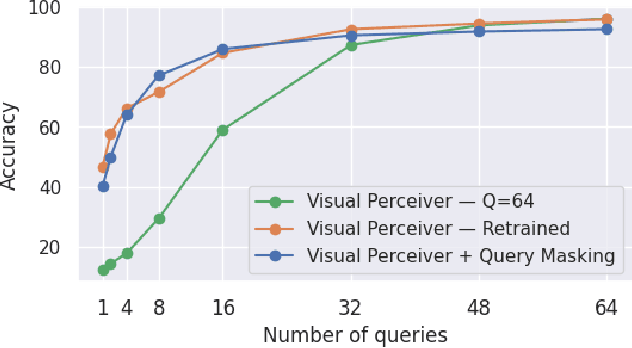
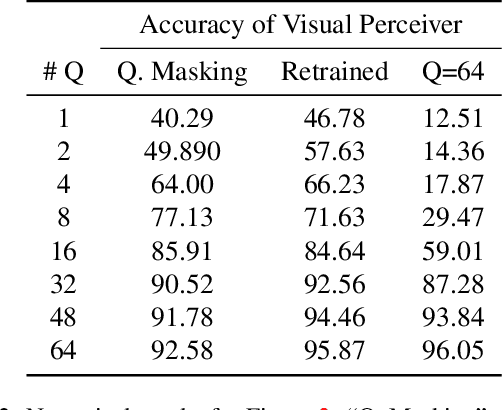
Transformers have been matching deep convolutional networks for vision architectures in recent works. Most work is focused on getting the best results on large-scale benchmarks, and scaling laws seem to be the most successful strategy: bigger models, more data, and longer training result in higher performance. However, the reduction of network complexity and inference time remains under-explored. The Perceiver model offers a solution to this problem: by first performing a Cross-attention with a fixed number Q of latent query tokens, the complexity of the L-layers Transformer network that follows is bounded by O(LQ^2). In this work, we explore how to make Perceivers even more efficient, by reducing the number of queries Q during inference while limiting the accuracy drop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge