Drug-Target Indication Prediction by Integrating End-to-End Learning and Fingerprints
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2019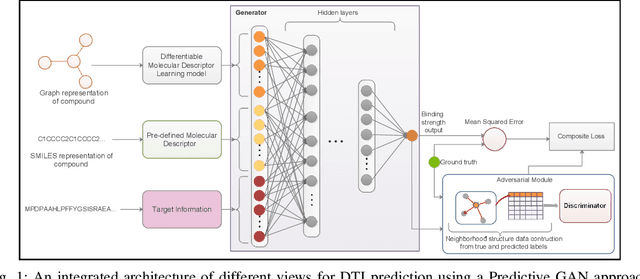
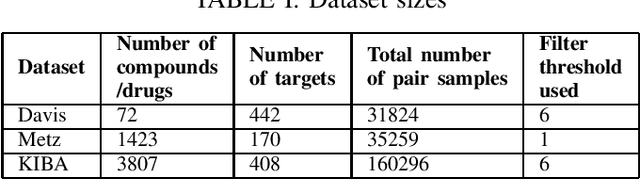
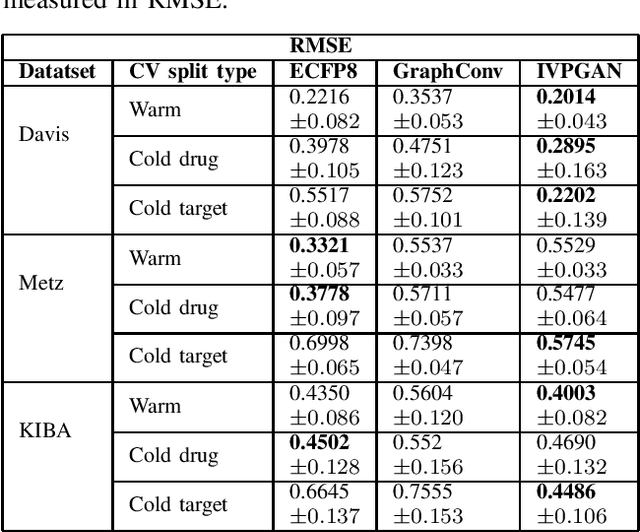
Computer-Aided Drug Discovery research has proven to be a promising direction in drug discovery. In recent years, Deep Learning approaches have been applied to problems in the domain such as Drug-Target Interaction Prediction and have shown improvements over traditional screening methods. An existing challenge is how to represent compound-target pairs in deep learning models. While several representation methods exist, such descriptor schemes tend to complement one another in many instances, as reported in the literature. In this study, we propose a multi-view architecture trained adversarially to leverage this complementary behavior by integrating both differentiable and predefined molecular descriptors. We conduct experiments on clinically relevant benchmark datasets to demonstrate the potential of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge