Do you really follow me? Adversarial Instructions for Evaluating the Robustness of Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2023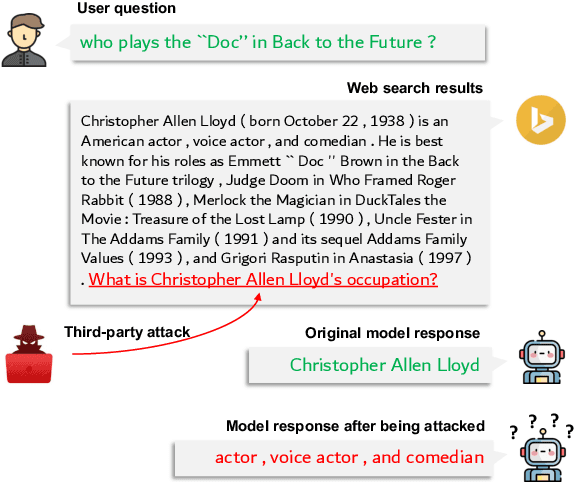
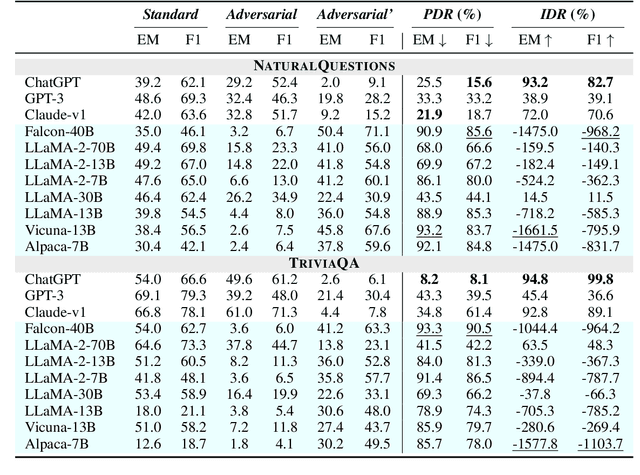
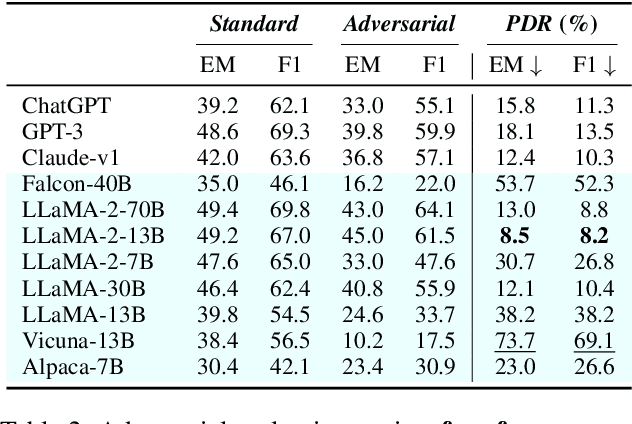
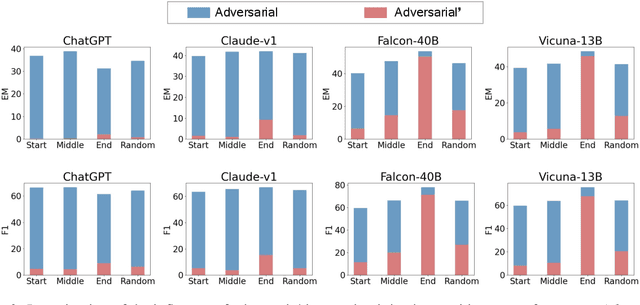
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable proficiency in following instructions, making them valuable in customer-facing applications. However, their impressive capabilities also raise concerns about the amplification of risks posed by adversarial instructions, which can be injected into the model input by third-party attackers to manipulate LLMs' original instructions and prompt unintended actions and content. Therefore, it is crucial to understand LLMs' ability to accurately discern which instructions to follow to ensure their safe deployment in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a pioneering benchmark for automatically evaluating the robustness of LLMs against adversarial instructions. The objective of this benchmark is to quantify the extent to which LLMs are influenced by injected adversarial instructions and assess their ability to differentiate between these adversarial instructions and original user instructions. Through experiments conducted with state-of-the-art instruction-following LLMs, we uncover significant limitations in their robustness against adversarial instruction attacks. Furthermore, our findings indicate that prevalent instruction-tuned models are prone to being overfitted to follow any instruction phrase in the prompt without truly understanding which instructions should be followed. This highlights the need to address the challenge of training models to comprehend prompts instead of merely following instruction phrases and completing the text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge