Do Convolutional Networks need to be Deep for Text Classification ?
Paper and Code
Jul 13, 2017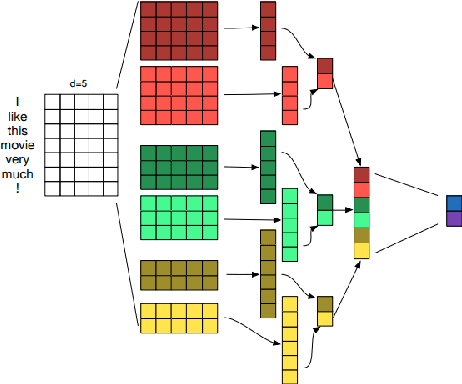
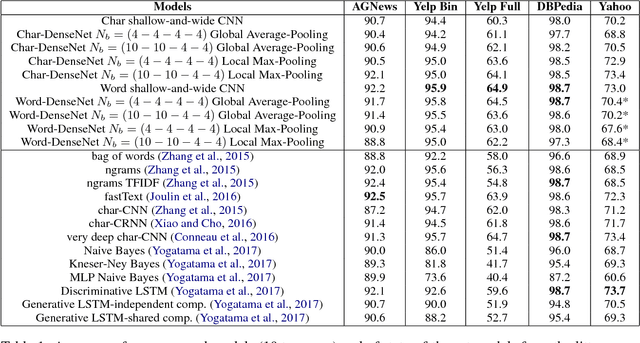
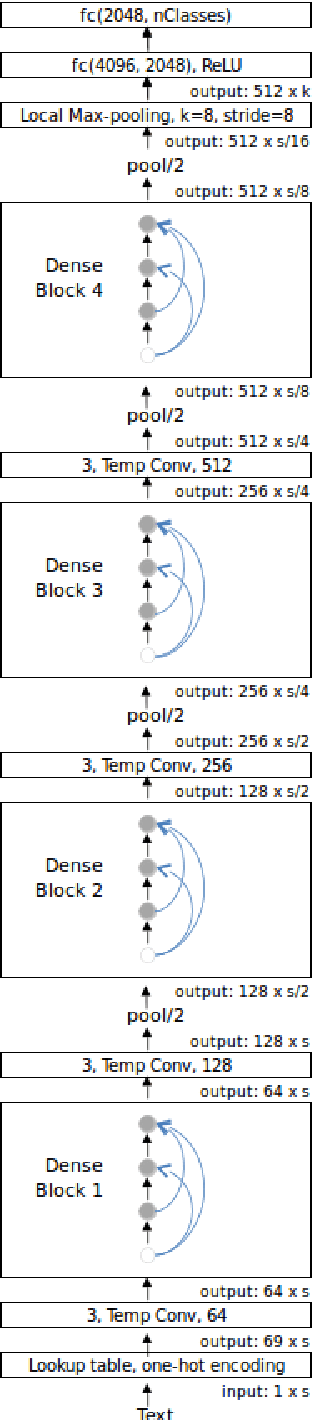
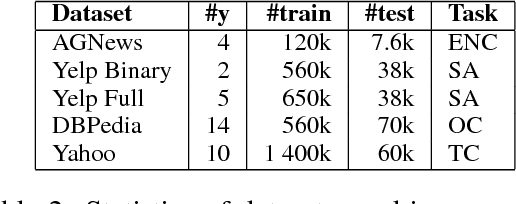
We study in this work the importance of depth in convolutional models for text classification, either when character or word inputs are considered. We show on 5 standard text classification and sentiment analysis tasks that deep models indeed give better performances than shallow networks when the text input is represented as a sequence of characters. However, a simple shallow-and-wide network outperforms deep models such as DenseNet with word inputs. Our shallow word model further establishes new state-of-the-art performances on two datasets: Yelp Binary (95.9\%) and Yelp Full (64.9\%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge