DNN-Based Semantic Model for Rescoring N-best Speech Recognition List
Paper and Code
Nov 02, 2020
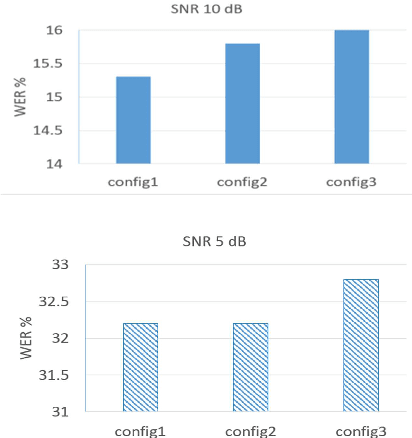
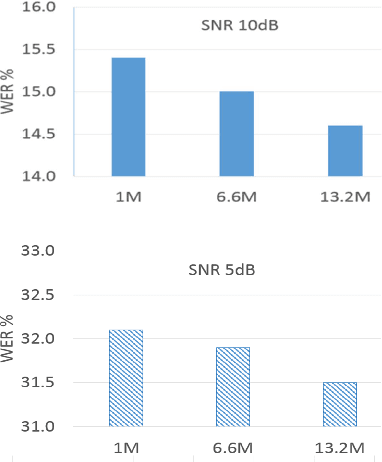
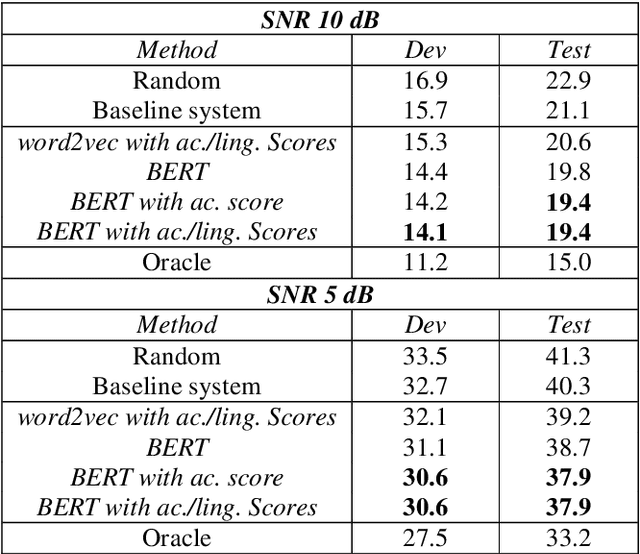
The word error rate (WER) of an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system increases when a mismatch occurs between the training and the testing conditions due to the noise, etc. In this case, the acoustic information can be less reliable. This work aims to improve ASR by modeling long-term semantic relations to compensate for distorted acoustic features. We propose to perform this through rescoring of the ASR N-best hypotheses list. To achieve this, we train a deep neural network (DNN). Our DNN rescoring model is aimed at selecting hypotheses that have better semantic consistency and therefore lower WER. We investigate two types of representations as part of input features to our DNN model: static word embeddings (from word2vec) and dynamic contextual embeddings (from BERT). Acoustic and linguistic features are also included. We perform experiments on the publicly available dataset TED-LIUM mixed with real noise. The proposed rescoring approaches give significant improvement of the WER over the ASR system without rescoring models in two noisy conditions and with n-gram and RNNLM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge