Dissecting liabilities in adversarial surgical robot failures: A national (Danish) and European law perspective
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2020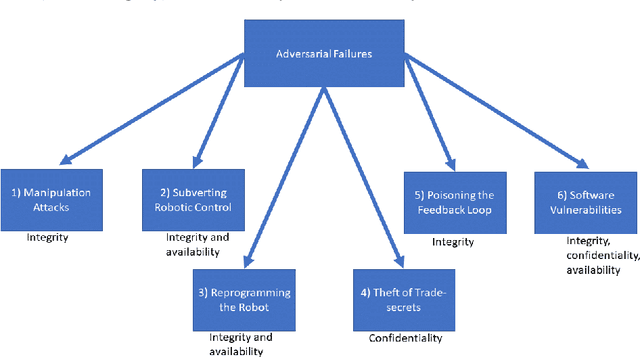

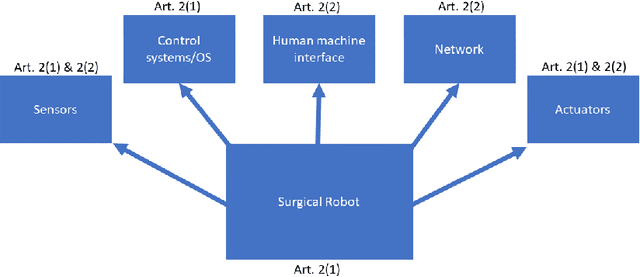
Being connected to a network exposes surgical robots to cyberattacks, which can damage the patient or the operator. These injuries are normally caused by safety failures, such as accidents with industrial robots, but cyberattacks are caused by security failures instead. Surgical robots are increasingly sold and used in the European Union, so we decide to uncover whether this change has been considered by EU law, and which legal remedies and actions a patient or manufacturer would have in a single national legal system in the union. We first conduct a case study, where we analyse which legal remedies a patient can make use of, if they are injured by a surgical robot caused by a cyberattack in the national legal system. We also explore whether cybersecurity and cyberattacks are considered by the upcoming Medical Device Regulation of the EU. We show that the selected national legal system is adequate. This is because of its flexibility and in a certain approach even to ignore the distinction between safety and security to the benefit of the patient, and in one situation to remove liability from the manufacturer by erasing its status as party. Otherwise, unless the operator or other parties have made the cyberattack more likely to occur, the manufacturer is liable. We find that the regulation does not directly consider security defects, requiring interpretation and use of guidance to show it. Due to the risk cyberattacks pose on medical equipment, we find this to not be adequate. We further find that the regulators of medical devices, including surgical robots, will not necessarily have adequate staff or rules of enforcement, as this has been left to the member states to solve. But, we also find, due to the comprehensive number of rules that can be applied cumulatively, together with the possibility for further rules and compliance later on, that these issues could be solved in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge